



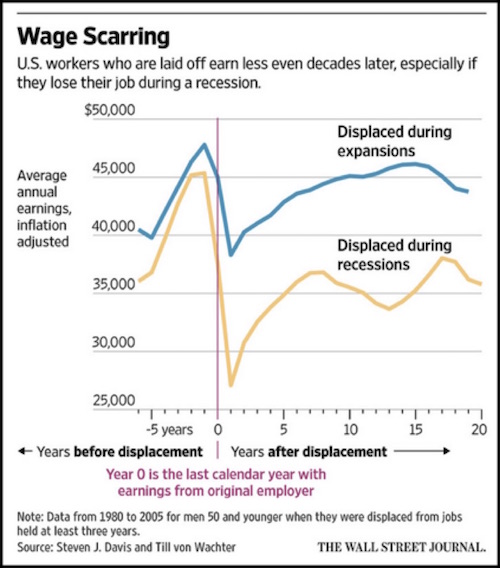
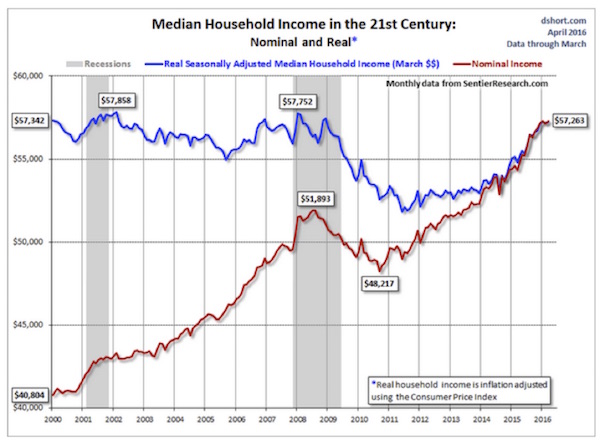
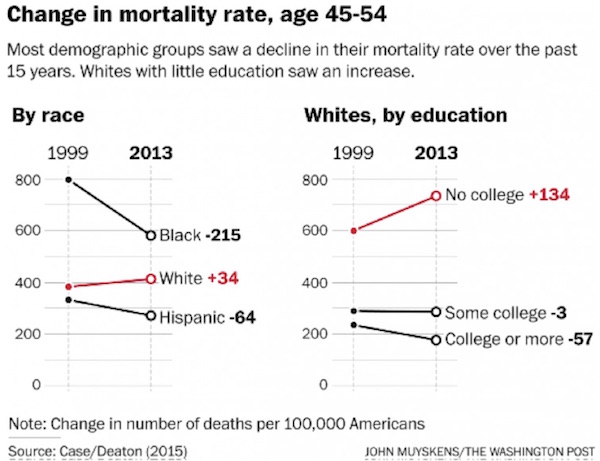
Nothing today is my 83rd birthday and off to
play tennis. Maybe I will get better line calls
today.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Very long-BUT, the true version of everything leading up to Obama's driven desire to capitulate to and appease Iran at any cost. (See 1 below.)
===
Mauldin on a variety of subjects. (See 2 below.)
====
Sent to me by a dear friend and fellow memo reader. (See 3 below.)
====
Who is Donald Trump and why don't we know as much about Obama? (See 4 below.)
====
I turned 83 today and Lynn surprised me at a friend's house and party with my favorite Key Lime Pie!



===
I have been urged by a very dear friend and fellow memo reader to get this book. I plan to do so but have some art book reading first. (See 5 below.)
===
Mauldin on a variety of subjects. (See 2 below.)
====
Sent to me by a dear friend and fellow memo reader. (See 3 below.)
====
Who is Donald Trump and why don't we know as much about Obama? (See 4 below.)
====
I turned 83 today and Lynn surprised me at a friend's house and party with my favorite Key Lime Pie!
===
I have been urged by a very dear friend and fellow memo reader to get this book. I plan to do so but have some art book reading first. (See 5 below.)
===
Dick
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
1) "Obama was here revealing his main rationale in 2012 for rejecting the Petraeus plan to arm the Syrian opposition that we examined earlier. Clearly, the president viewed the anti-Assad movement in Syria just as he had viewed the Green Movement in Iran three years earlier: as an impediment to realizing the strategic priority of guiding Iran to the path of success. Was the Middle East in fact polarized between the Iranian-led alliance and just about everyone else? Yes. Were all traditional allies of the United States calling for him to stand up to Iran? Yes. Did the principal members of his National Security Council recommend as one that the United States heed the call of the allies? Again, yes. But Obama’s eyes were still locked on the main prize: the grand bargain with Tehran."
"The same desire to accommodate Iran has tailored Obama’s strategy toward the terrorist group Islamic State.
That, too, has not received the attention it deserves."
"Meanwhile, the president is depicting his congressional critics as irresponsible warmongers. He would have us believe that there are only two options: his undeclared détente with Iran and yet another war in the Middle East. This is a false choice. It ignores the one policy that every president since Jimmy Carter has pursued till now: vigorous containment on all fronts, not just in the nuclear arena. Obama, however, is intent on obscuring this option, and for a simple reason: an honest debate about it would force him to come clean with the American people and admit the depth of his commitment to the strategy whose grim results are multiplying by the day.
Why the need to bypass Congress? Rhodes had little need to elaborate. As the president himself once noted balefully, “[T]here is hostility and suspicion toward Iran, not just among members of Congress but the American people”—and besides, “members of Congress are very attentive to what Israel says on its security issues.” And that “hostility and suspicion” still persist, prompting the president in his latest State of the Union address to repeat his oft-stated warning that he will veto “any new sanctions bill that threatens to undo [the] progress” made so far toward a “comprehensive agreement” with the Islamic Republic.
As far as the president is concerned, the less we know about his Iran plans, the better. Yet those plans, as Rhodes stressed, are not a minor or incidental component of his foreign policy. To the contrary, they are central to his administration’s strategic thinking about the role of the United States in the world, and especially in the Middle East.
One sympathizes with Gelb’s sense of alarm, but his premises are mistaken. Inexperience is a problem in this administration, but there is no lack of strategic vision. Quite the contrary: a strategy has been in place from the start, and however clumsily it may on occasion have been implemented, and whatever resistance it has generated abroad or at home, Obama has doggedly adhered to the policies that have flowed from it.
In what follows, we’ll trace the course of the most important of those policies and their contribution to the president’s announced determination to encourage and augment Iran’s potential as a successful regional power and as a friend and partner to the United States.
2009-2010: Round One, Part I
In the giddy aftermath of Obama’s electoral victory in 2008, anything seemed possible. The president saw himself as a transformational leader, not just in domestic politics but also in the international arena, where, as he believed, he had been elected to reverse the legacy of his predecessor, George W. Bush. To say that Obama regarded Bush’s foreign policy as anachronistic is an understatement. To him it was a caricature of yesteryear, the foreign-policy equivalent of Leave It to Beaver. Obama’s mission was to guide America out of Bushland, an arena in which the United States assembled global military coalitions to defeat enemies whom it depicted in terms like “Axis of Evil,” and into Obamaworld, a place more attuned to the nuances, complexities, and contradictions—and opportunities—of the 21st century. In today’s globalized environment, Obama told the United Nations General Assembly in September 2009, “our destiny is shared, power is no longer a zero-sum game. No one nation can or should try to dominate another nation. . . . No balance of power among nations will hold.”
If, in Bushland, America had behaved like a sheriff, assembling a posse to go in search of monsters, in Obamaworld America would disarm its rivals by ensnaring them in a web of cooperation.
For the new president, nothing revealed the conceptual inadequacies of Bushland more clearly than the 2003 invasion of Iraq. Before coming to Washington, Obama had opposed the toppling of the Iraqi dictator Saddam Hussein; once in the U.S. Senate, he rejected Bush’s “surge” and introduced legislation to end the war. Shortly after his inauguration in January 2009, he pledged to bring the troops home quickly—a commitment that he would indeed honor. But if calling for withdrawal from Iraq had been a relatively easy position to take for a senator, for a president it raised a key practical question: beyond abstract nostrums like “no nation can . . . dominate another nation,” what new order should replace the American-led system that Bush had been building?
This was, and remains, the fundamental strategic question that Obama has faced in the Middle East, though one would search his speeches in vain for an answer to it. But Obama does have a relatively concrete vision. When he arrived in Washington in 2006, he absorbed a set of ideas that had incubated on Capitol Hill during the previous three years—ideas that had received widespread attention thanks to the final report of the Iraq Study Group, a bipartisan congressional commission whose co-chairs, former secretary of state James Baker and former Indiana congressman Lee Hamilton, interpreted their mission broadly, offering advice on all key aspects of Middle East policy.
The report, published in December 2006, urged then-President Bush to take four major steps: withdraw American troops from Iraq; surge American troops in Afghanistan; reinvigorate the Arab-Israeli “peace process”; and, last but far from least, launch a diplomatic engagement of the Islamic Republic of Iran and its junior partner, the Assad regime in Syria. Baker and Hamilton believed that Bush stood in thrall to Israel and was therefore insufficiently alive to the benefits of cooperating with Iran and Syria. Those two regimes, supposedly, shared with Washington the twin goals of stabilizing Iraq and defeating al-Qaeda and other Sunni jihadi groups. In turn, this shared interest would provide a foundation for building a concert system of states—a club of stable powers that could work together to contain the worst pathologies of the Middle East and lead the way to a sunnier future.
Expressing the ethos of an influential segment of the foreign-policy elite, the Baker-Hamilton report became the blueprint for the foreign policy of the Obama administration, and its spirit continues to pervade Obama’s inner circle. Denis McDonough, now the president’s chief of staff, once worked as an aide to Lee Hamilton; so did Benjamin Rhodes, who helped write the Iraq Study Group’s report. Obama not only adopted the blueprint but took it one step further, recruiting Vladimir Putin’s Russia as another candidate for membership in the new club. The administration’s early “reset” with Russia and its policy of reaching out to Iran and Syria formed two parts of a single vision. If, in Bushland, America had behaved like a sheriff, assembling a posse (“a coalition of the willing”) to go in search of monsters, in Obamaworld America would disarm its rivals by ensnaring them in a web of cooperation. To rid the world of rogues and tyrants, one must embrace and soften them.

How would this work in the case of Iran? During the Bush years, an elaborate myth had developed according to which the mullahs in Tehran had themselves reached out in friendship to Washington, offering a “grand bargain”: a deal on everything from regional security to nuclear weapons. The swaggering Bush, however, had slapped away the outstretched Iranian hand, squandering the opportunity of a lifetime to normalize U.S.-Iranian relations and thereby bring order to the entire Middle East.
Unfortunately, the Supreme Leader of Iran, Ali Khamenei, ignored the president’s invitation. Five months later, in June 2009, when the Green Movement was born, his autocratic fist was still clenched. As the streets of Tehran exploded in the largest anti-government demonstrations the country had seen since the revolution of 1979, he used that fist to beat down the protesters. For their part, the protesters, hungry for democratic reform and enraged by government rigging of the recent presidential election, appealed to Obama for help. He responded meekly, issuing tepid statements of support while maintaining a steady posture of neutrality. To alienate Khamenei, after all, might kill the dream of a new era in U.S.-Iranian relations.
If this show of deference was calculated to warm the dictator’s heart, it failed. “What we intended as caution,” one of Obama’s aides would later tell a reporter, “the Iranians saw as weakness.” Indeed, the president’s studied “caution” may even have emboldened Tehran to push forward, in yet another in the long series of blatant violations of its obligations under the nuclear Nonproliferation Treaty (NPT), with its construction of a secret uranium enrichment facility in an underground bunker at Fordow, near Qom.
When members of Iran’s Green Movement appealed to Obama for help in 2009, he responded meekly—after all, to alienate Khamenei might kill the dream of a new era in U.S.-Iranian relations.
This time, Obama reacted. Revealing the bunker’s existence, he placed Khamenei in a tough spot. The Russians, who had been habitually more lenient toward the Iranian nuclear program than the Americans, were irritated by the disclosure of this clandestine activity; the French were moved to demand a strong Western response.
Obama, it seemed to some, had pulled off a major coup. Less than a year after taking office, he was turning his vision of a new Middle East order into a reality. Or was he? Once the heat was off, Khamenei reneged on the deal, throwing the president back to square one and in the process weakening him politically at home, where congressional skeptics of his engagement policy now began lobbying for more stringent economic sanctions on Tehran. To protect his flank, Obama tacked rightward, appropriating, if with visible reluctance, some of his opponents’ rhetoric and bits of their playbook as well. In 2010, he signed into law the Comprehensive Iran Sanctions, Accountability, and Divestment Act (CISADA), which eventually would prove more painful to Iran than any previous measure of its kind.
In later years, whenever Obama would stand accused of being soft on Iran, he would invariably point to CISADA as evidence to the contrary. “[O]ver the course of several years,” he stated in March 2014, “we were able to enforce an unprecedented sanctions regime that so crippled the Iranian economy that they were willing to come to the table.” The “table” in question was the negotiation resulting in the November 2013 agreement, known as the Joint Plan of Action (JPOA), which we shall come to in due course. But masked in the president’s boast was the fact that he had actually opposed CISADA, which was rammed down his throat by a Senate vote of 99 to zero.
Once the bill became law, a cadre of talented and dedicated professionals in the Treasury Department set to work implementing it. But the moment of presumed “convergence” between Obama and his congressional skeptics proved temporary and tactical; their fundamental difference in outlook would become much more apparent in the president’s second term. For the skeptics, the way to change Khamenei’s behavior was to place him before a stark choice: dismantle Iran’s nuclear program—period—or face catastrophic consequences. For Obama, to force a confrontation with Khamenei would destroy any chance of reaching an accommodation on the nuclear front and put paid to his grand vision of a new Middle East order.
“The hardest cross I have to bear is the Cross of Lorraine,” Winston Churchill supposedly cracked about managing his wartime relations with Charles de Gaulle. As Obama sees it, his hardest cross to bear has been the Star of David, represented by Israel’s prime minister Benjamin Netanyahu.
To the Israelis, who have long regarded Iran’s nuclear program as an existential threat, Obama’s engagement policy was misguided from the start. Their assessment mattered, because influential Americans listened to them. What was more, American Jews constituted an important segment of the Democratic party’s popular base and an even more important segment of its donors. In the election year of 2012, for Obama to be perceived as indifferent to Israeli security would jeopardize his prospects of a second term—and hardly among Jews alone.
When the Israelis threatened to attack Iran, Obama responded by putting Israel in a bear hug. From one angle, it looked like an expression of friendship. From another, like an effort to break Netanyahu’s ribs.
The Israelis did more than just criticize Obama; they also threatened to take action against Iran that would place the president in an intolerable dilemma. In 2011, Ehud Barak, the defense minister at the time, announced that Iran was quickly approaching a “zone of immunity,” meaning that its nuclear program would henceforth be impervious to Israeli attack. As Iran approached that zone, Israel would have no choice but to strike. And what would America do then? The Israeli warnings grew ever starker as the presidential election season heated up. Netanyahu, it seemed, was using the threat of Israeli action as a way of prodding Washington itself to take a harder line.
From another angle, however, the bear hug looked like an effort to break Netanyahu’s ribs. Even while expressing affection for Israel, Obama found ways to signal his loathing for its prime minister. During one tense meeting at the White House, for example, the president abruptly broke off to join his family for dinner, leaving Netanyahu to wait for him alone. In mitigation, Obama supporters would adduce ongoing friction between the two countries over West Bank settlements and peace negotiations with the Palestinians. This was true enough, but the two men differed on quite a number of issues, among which Iran held by far the greatest strategic significance. In managing the anxieties of his liberal Jewish supporters, Obama found it useful to explain the bad atmosphere as a function of Netanyahu’s “extremism” rather than of his own outreach to Iran—to suggest, in effect, that if only the hothead in the room would sit down and shut up, the grownups could proceed to resolve the Iranian nuclear problem along reasonable lines.
The tactic proved effective. At least for the duration, Obama prevented Israel from attacking Iran; preserved American freedom of action with regard to Iran’s nuclear program; and kept his disagreements with the Israeli government within the comfort zone of American Jewish Democrats.
When Obama strode into office and announced his desire to kiss the snake, the Saudis lost no time in making their displeasure felt. Three months later, the king responded gruffly to an extensive presentation on Obama’s outreach program by Dennis Ross, then a senior official in the State Department with responsibility for Iran. “I am a man of action,” Abdullah said according to a New York Times report. “Unlike you, I prefer not to talk a lot.” He then posed a series of pointed questions that Ross could not answer. “What is your goal? What will you do if this does not work? What will you do if the Chinese and the Russians are not with you? How will you deal with Iran’s nuclear program if there is not a united response?” The questions added up to a simple point: your Iran policy is based on wishful thinking.
As it happens, one traditional American ally in the region was—at least at first—untroubled by Obama’s policy of Iran engagement: the Turkish leader Recep Tayyip Erdoğan. Indeed, Erdoğan found much to extol in the new American initiative, which dovetailed perfectly with his own foreign policy of “zero problems with [Arab and Muslim] neighbors.” Among other things, Erdoğan meant to establish Ankara as the middleman between the United States and Iran and Syria, Turkey’s traditional adversaries. This vision nested so comfortably within Obama’s planned concert system that Erdoğan quickly became one of the few international personalities with whom Obama developed a close personal rapport.
Contrary to what observers have long assumed, Obama does connect his Iran policy and his Syria policy: just as he showed deference to Iran on the nuclear front, he has deferred to the Iranian interest in Syria.
The director of the CIA, David Petraeus, responded to this request by America’s regional allies with a plan to train and equip Syrian rebels in Jordan and to assist them once back in Syria. Defense Secretary Leon Panetta, Secretary of State Hillary Clinton, and General Martin Dempsey, the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, all supported the Petraeus plan. But Obama rejected it.
Why? Undoubtedly the president had a mix of reasons and possible motives, which were the objects of extensive speculation in the media. But one motive was never included in the list: namely, his fear of antagonizing Iran. For the longest time, it was simply assumed that Obama drew no connection between his Iran policy and his Syria policy. This, however, was not the case. In fact—as we shall see below—just as, from the beginning, he showed deference to Iran on the nuclear front, he showed the same deference to the Iranian interest in Syria.

An ostensible thaw in American-Iranian relations occurred early in the president’s second term. To hear him tell it today, what precipitated the thaw was a strategic shift by Tehran on the nuclear front. In his version of the story—let’s call it the “official version”—two factors account for the Iranian change of heart. One of them was American coercive diplomacy; the other was a new spirit of reform in Tehran. And the two were interrelated. The first, as Obama himself explained in the March 2014 interview cited earlier, had taken the form of “an unprecedented sanctions regime that so crippled the Iranian economy that [the Iranians] were willing to come to the table.” The second was a corollary of the first. The same sanctions regime had also helped bring to power the new government of Hassan Rouhani, whose moderate approach would in turn culminate in the November 2013 signing of the interim nuclear deal, which “for the first time in a decade halts their nuclear program.”
The turning point in the American-Iranian relationship was not, as the official version would have it, the election of Hassan Rouhani in June 2013. It was the reelection of Barack Obama in November 2012.
In early 2013, at the outset of his second term, Obama developed a secret bilateral channel to Ahmadinejad’s regime. When the full impact of this is taken into account, a surprising fact comes to light. The turning point in the American-Iranian relationship was not, as the official version would have it, the election of Hassan Rouhani in June 2013. It was the reelection of Barack Obama in November 2012.
Indeed, the first secret meeting with the Iranians (that is, the first we know of) took place even earlier, in early July 2012, eleven months before Rouhani came to power. Jake Sullivan, who at the time was the director of policy planning in Hillary Clinton’s State Department, traveled secretly to Oman to meet with Iranian officials. The Obama administration has told us next to nothing about Sullivan’s meeting, so we are forced to speculate about the message that he delivered.
Most pertinent is the timing. At that moment, pressure was mounting on the president to intervene in Syria. Sullivan probably briefed the Iranians on Obama’s strong desire to stay out of that conflict, and may have sought Tehran’s help in moderating Assad’s behavior. But summer 2012 was also the height of the American presidential campaign. Perhaps Sullivan told the Iranians that the president was keen to restart serious nuclear negotiations after the election. Recall that this meeting took place shortly after a hot microphone had caught Obama saying to Dmitry Medvedev, the Russian president, “On all these issues, but particularly missile defense, this can be solved, but it’s important . . . to give me space. This is my last election. After my election, I have more flexibility.”
Did Sullivan give the Iranians a similar message? Did he tell Ahmadinejad’s officials that Obama’s need to secure the pro-Israel vote had forced him to take a deceptively belligerent line toward Iran? That Iran had nothing to fear from an Israeli attack? That after the election Obama would demonstrate even greater flexibility on the nuclear issue?
Whatever the answers to these questions, it is a matter of record that Obama opened his second term with a campaign of outreach to Tehran—a campaign that was as intensive as it was secret. By February 2013, a month after his inauguration, the backchannel was crowded with American officials. Not just Sullivan, but Deputy Secretary of State William Burns, National Security Council staffer Puneet Talwar, State Department non-proliferation adviser Robert Einhorn, and Ambassador to the United Nations Susan Rice were all engaging their Iranian counterparts.
According to the official version, this stampede toward Tehran had no impact on Iranian-American relations. Nothing notable occurred in that realm, we are told, until the arrival on the scene of Rouhani. In fact, however, it was during this earlier period that Obama laid the basis for the November 2013 Joint Plan of Action. And that agreement was the product of three American concessions—two of which, and possibly the third as well, were made long before Rouhani ever came to power.
In April 2013, the Americans and their P5+1 partners met with Iranian negotiators in Almaty, Kazakhstan, where they offered to relieve the sanctions regime in exchange for the elimination of Iran’s stockpiles of uranium that had already been enriched to 20 percent. This was concession number one, bowing to the longstanding Iranian demand for economic compensation immediately, before a final agreement could be reached. Even more important was concession number two, which permitted the Iranians to continue enriching uranium to levels of 5 percent—this, despite the fact that six United Nations Security Council resolutions had ordered Iran to cease all enrichment and reprocessing activities.
Iranian negotiators rejected these two gifts—or, rather, they pocketed them and demanded a third, the one they coveted the most. Hailing the proposals by their counterparts as a step in the right direction, they criticized them for failing to stipulate the Iranian “right to enrich.” There was a difference, they argued, between temporarily permitting Iran to enrich uranium to 5 percent and recognizing its inalienable right to do so. If Obama wanted a deal, he would have to agree to shred the Security Council resolutions by offering, up front, an arrangement that would end the economic sanctions on Iran entirely and that would allow the Iranians to enrich uranium in perpetuity.
By exaggerating the spirit of reform in Tehran, the White House was able to suggest that Iran, and not America, had compromised.
Obama’s acceptance of this condition, the third and most important American gift, is what made the Joint Plan of Action possible. The American negotiators transmitted the president’s acceptance to the Iranians in the backchannel, and then John Kerry sprang it on his hapless negotiating partners in November. We do not know when, precisely, Obama made this offer, but the Iranians set their three conditions before Rouhani took office.
Round Two: Iran, Syria, and Islamic State
The nuclear issue wasn’t the only tender spot in U.S.-Iran relations in this period. Before returning to it, let’s look briefly at two other regional fronts.
Obama’s second term has also included efforts to accommodate Iran over Syria. Susan Rice, by now the president’s national-security adviser, inadvertently admitted as much in an address she delivered on September 9, 2013, a few weeks after Bashar Assad had conducted a sarin-gas attack on Ghouta, a suburb outside Damascus, that killed approximately 1,500 civilians. Reviewing past American efforts to restrain the Syrian dictator, Rice blithely depicted Tehran as Washington’s partner. “At our urging, over months, Russia and Iran repeatedly reinforced our warning to Assad,” she explained. “We all sent the same message again and again: don’t do it.”
Why did Obama back off on strikes against Syria? Could it have been fear of scuttling the biggest—and still secret—foreign-policy initiative of his entire presidency?
Rice’s remarks were disingenuous. In reality, the Islamic Republic was then precisely what it remains today, namely, the prime enabler of Assad’s murder machine. But Rice’s intention was not to describe Iranian behavior accurately. In addition to accustoming the American press and foreign-policy elite to the idea that Iran was at least a potential partner, her speech was aimed at influencing Congress’s deliberation of air strikes against Syria—strikes that Obama had abruptly delayed a week and a half earlier in what will certainly be remembered as one of the oddest moments of his presidency.
The oddity began shortly after Obama sent Secretary of State John Kerry out to deliver a Churchillian exhortation on the theme of an impending American attack. While that speech was still reverberating, the president convened a meeting of his inner circle in the Oval Office, where he expressed misgivings about the policy that his Secretary of State had just announced. Curiously, the meeting did not include either Kerry or Secretary of Defense Chuck Hagel, the principal members of his senior national-security staff. Obama then invited Denis McDonough to break away from the others and join him for a private walk around the White House grounds. On his return, Obama stunned the waiting group with the news that he had decided to delay the strikes on Assad in order to seek congressional approval.
What thoughts did Obama share with McDonough? We can dispense with the official explanation, which stresses the president’s principled belief in the need to consult the legislative branch on matters of war and peace. That belief had played no part in previous decisions, like the one to intervene in Libya. Clearly, Obama was hiding behind Congress in order either to delay action or to kill it altogether. The true reasons for the delay were evidently too sensitive even for the ears of his closest national-security aides. Could they have included fear of scuttling the biggest—and still secret—foreign-policy initiative of his second term, possibly of his entire presidency?
In the event, the punt to Congress bought Obama some time, but at a significant political cost. At home the decision made him appear dithering and weak; on Capitol Hill, Democrats quietly fumed over the way the White House was abruptly ordering them out on a limb. In Syria, Assad crowed with delight as his opponents crumpled in despair. Elsewhere, American allies felt exposed and vulnerable, wondering whether Obama would ever truly come to their aid in a pinch.
As we know, Obama’s quandary would become Moscow’s opportunity. Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov offered the president a way to regain his balance. Russia and the United States, Lavrov proposed, would cooperate to strip Assad of his sarin gas. From the sidelines, the Iranians publicly applauded the proposal, and Obama jumped to accept it.
But the deal was a quid pro quo. In return for a minor (though highly visible) concession from Assad, Obama tacitly agreed not to enter the Syrian battlefield. In effect, the Russians, Assad, and the Iranians were offering him, and he was accepting, surrender with honor, enabling him to say later, with a straight face, that the episode was a successful example of his coercive diplomacy. “Let’s be very clear about what happened,” he bragged in his March 2014 interview. “I threatened [sic] kinetic strikes on Syria unless they got rid of their chemical weapons.” In reality, Assad only gained—and gained big. Obama immediately muted his calls for Assad to step down from power, and his behavior thoroughly demoralized the Syrian opposition. Nor did the deal stop Assad from launching further chemical attacks. Once deprived of his sarin stockpiles, he simply switched to chlorine.
This was fictive. Obama made it sound as if Tehran was eager to punish Assad for his use of chemical weapons, but nothing could have been farther from the truth. Even as he was speaking, Iran was publicly blaming the Syrian rebels, not Assad, for the Ghouta attack. Nor was stopping the slaughter ever the president’s true goal. From his perspective, he did not have the power to prevent Assad’s atrocities. He did, however, have the sense to recognize a good thing when he saw it. The opportunity to join with Iran in an ostensibly cooperative venture was too good to let slip away—and so he seized it.
That Obama has treated Syria as an Iranian sphere of interest all along has been brought home in a recent report in the Wall Street Journal. In August 2014, according to the Journal, the president wrote a letter to Ali Khamenei, acknowledging the obstacle to their cooperation presented by the nuclear impasse but taking pains to reassure Khamenei regarding the fate of Assad, his closest ally. American military operations inside Syria, he wrote, would target neither the Syrian dictator nor his forces.
This element of the president’s thinking has received remarkably little attention, even though Obama himself pointed to it directly in a January 2014 interview with David Remnick, the editor of theNew Yorker. The Arab states and Israel, Obama said then, wanted Washington to be their proxy in the contest with Iran; but he adamantly refused to play that role. Instead, he envisioned, in Remnick’s words, “a new geostrategic equilibrium, one less turbulent than the current landscape of civil war, terror, and sectarian battle.” Who would help him develop the strategy to achieve this equilibrium? “I don’t really even need George Kennan right now,” the president responded, alluding to the acknowledged godfather of the cold-war strategy of containment. What he truly needed instead were strategic partners, and a prime candidate for that role was—he explained—Iran.

The same desire to accommodate Iran has tailored Obama’s strategy toward the terrorist group Islamic State. That, too, has not received the attention it deserves.
Last June, when Islamic State warriors captured Mosul in northern Iraq, the foreign-policy approval ratings of the president plummeted, and Obama’s critics claimed, not for the first time, that he had no strategy at all. Ben Rhodes sprang to his defense, suggesting that despite appearances to the contrary, the administration actually had a plan, if a hitherto unannounced one. “We have longer-run plays that we’re running,” he said. “Part of this is keeping your eye on the long game even as you go through tumultuous periods.”
The administration has subtly exploited the rise of the Islamic State to elevate Obama’s outreach to Iran. Behind the scenes, coordination and consultation have reached new heights.
Rhodes offered no details, and subsequent events seemed to confirm the impression that Obama actually had no long game. In addition to being caught flat-footed by Islamic State, moreover, he was reversing himself on other major issues: sending troops back to Iraq after having celebrated their homecoming, ordering military operations in Syria that he had opposed for years. How could such reversals be consistent with a long game?
Meanwhile, so have expressions of dissatisfaction with traditional allies for taking positions hostile to Iran. Our “biggest problem” in Syria is our own regional allies, Vice President Joseph Biden complained to students at Harvard University in early October. Turkey, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates were “so determined to take down Assad” that they were pouring “hundreds of millions of dollars and tens of thousands of tons of weapons” into the Syrian opposition. A few weeks later, a senior Obama administration official cuttingly described another ally, Israel’s prime minister, as “a chickenshit,” and a second official, similarly on the record, bragged about the success of the United States in shielding the Islamic Republic from Israel. “[U]ltimately [Netanyahu] couldn’t bring himself to pull the trigger. It was a combination of our pressure and his own unwillingness to do anything dramatic. Now it’s too late.”
Of course, administration officials routinely insist that the United States is not working with Tehran. The coordination, however, is impossible to disguise. Thus, when Iranian jets recently appeared in Iraqi skies, they professed ignorance. Reporters, noting that the jets were flying sorties in the same air space as American jets and striking related targets, asked the Pentagon spokesman how the American and Iranian air forces could work in the same space without colliding. “We are flying missions over Iraq, [and] we coordinate with the Iraqi government as we conduct those,” said the spokesman. “It’s up to the Iraqi government to de-conflict that airspace.” When Kerry was asked about the news that the Iranian air force was operating in Iraq, he responded that this was a “net positive.”
A positive? With American acquiescence, Iran is steadily taking control of the security sector of the Iraqi state. Soon it will dominate the energy sector as well, giving it effective control over the fifth largest oil reserves in the world. When the announced goal of the United States is to build up a moderate Sunni bloc capable of driving a wedge between Islamic State and the Sunni communities, aligning with Iran is politically self-defeating. In both Iraq and Syria, Iran projects its power through sectarian militias that slaughter Sunni Muslims with abandon. Are there any Sunni powers in the region that see American outreach to Tehran as a good thing? Are there any military-aged Sunni men in Iraq and Syria who now see the United States as a friendly power? There are none.
The approach is detrimental to American interests in other arenas as well. We received a portent of things to come on January 18 of this year, when the Israel Defense Forces struck a convoy of senior Hizballah and Iranian officers, including a general in the Revolutionary Guards, in the Golan Heights. Ten days later, Hizballah and Iran retaliated. In other words, by treating Syria as an Iranian sphere of interest, Obama is allowing the shock troops of Iran to dig in on the border of Israel—not to mention the border of Jordan. The president’s policy assumes that Israel and America’s other allies will hang back quietly while Iran takes southern Syria firmly in its grip. They will not; to assume otherwise is folly.
Round Three: 2015-
In November 2013, when Obama purchased the participation of Iran in the Joint Plan of Action, he established a basic asymmetry that has remained a key feature of the negotiations ever since. He traded permanent American concessions for Iranian gestures of temporary restraint.
The most significant such gestures by Iran were to dilute its stockpiles of uranium enriched to 20 percent; to refrain from installing new centrifuges; and to place a hold on further construction of the Arak plutonium reactor. All three, however, can be easily reversed. By contrast, the Americans recognized the Iranian right to enrich and agreed to the principle that all restrictions on Iran’s program would be of a limited character and for a defined period of time. These two concessions are major, and because they are not just the policy of the United States government but now the collective position of the permanent members of the United Nations Security Council and Germany, they will likely never be reversed.
In his negotiations with Iran, the president has traded major American concessions for Iranian gestures of temporary restraint. These concessions will likely never be reversed.
Obama has repeatedly stated, most recently in his 2015 State of the Union address, that the interim agreement “halted” the Iranian nuclear program. Or, as he put it in his March 2014 interview, the “logic” of the JPOA was “to freeze the situation for a certain period of time to allow the negotiators to work.” But the agreement froze only American actions; it hardly stopped the Iranians from moving forward.
For one thing, the JPOA restricts the program only with respect to enrichment capacity and stockpiles; it is entirely silent about the military components: ballistic missiles, procurement, warhead production. For another, to call what the JPOA achieved even in these limited domains “a freeze” is a gross exaggeration. Iranian nuclear scientists have continued to perfect their craft. They are learning how to operate old centrifuges with greater efficiency. And thanks to a loophole in the JPOA permitting work on “research and development,” they are also mastering the use of new, more effective centrifuges.
Therefore, the Iranian nuclear program is poised to surge ahead. The moment the JPOA lapses—a date first scheduled for July 2014, then rescheduled to November 2014, then re-rescheduled to June 30 of this year, possibly to be re-re-rescheduled yet again—Iran will be in a stronger position than before the negotiations began. This fact gives Tehran considerable leverage over Washington during the next rounds.
We can say with certainty that Obama has had no illusions about this asymmetry—that he conducted the negotiations with his eyes wide open—because the White House took pains to hide the truth from the American public. In 2013, instead of publishing the text of the JPOA, it issued a highly misleading fact sheet. Peppered with terms like “halt,” “roll back,” and “dismantle,” the document left the impression that the Iranians had agreed to destroy their nuclear program.
The Iranian foreign minister, however, refused to play along. He protested—loudly and publicly. “The White House version both underplays the [American] concessions and overplays Iranian commitments,” Javad Zarif correctly told a television interviewer. “The White House tries to portray it as basically a dismantling of Iran’s nuclear program. That is the word they use time and again.” He defied the interviewer to “find a . . . single word that even closely resembles dismantling or could be defined as dismantling in the entire text.”
President Rouhani went even further. In an interview with CNN’s Fareed Zakaria, he emphasized not just that Iran had refused to destroy centrifuges within the terms of the JPOA, but that it would never destroy them “under any circumstances.” Currently Iran has approximately 9,000 centrifuges installed and spinning, and roughly 10,000 more installed but inactive. Until Rouhani made his statement, the Obama administration had led journalists to believe that the final agreement would force the Iranians to dismantle some 15,000 centrifuges.Rouhani disabused the world of those expectations.
“This strikes me as a train wreck,” a distraught Zakaria exclaimed after the interview. “This strikes me as potentially a huge obstacle because the Iranian conception of what the deal is going to look like and the American conception now look like they are miles apart.” Not long thereafter, as if to confirm the point, Ali Khamenei called for an outcome that will permit the development of an industrial-sized nuclear program over the next decade.

Khamenei’s hard line no doubt came as a surprise to Obama. When the president first approved the JPOA, he failed to recognize a key fact: his twin goals of liberating Iran from its international isolation and stripping the Islamic Republic of its nuclear capabilities were completely at odds with each other. From Obama’s perspective, he was offering Khamenei an irresistible deal: a strategic accommodation with the United States. Iran analysts had led the president to believe that Khamenei was desperate for just such an accommodation, and to achieve that prize he was searching only for a “face-saving” nuclear program—one that would give him a symbolic enrichment capability, nothing more. What soon became clear, however, was that Khamenei was betting that Obama would accommodate Iran even if it insisted on, and aggressively pursued, an industrial-scale program.
Over the last year, Obama has reportedly allowed Iran to retain, in one form or another, its facilities at Natanz, Fordow, and Arak—sites that Iran built in flagrant violation of the NPT to which it is a signatory. This is the same Obama who declared at the outset of negotiations that the Iranians “don’t need to have an underground, fortified facility like Fordow in order to have a peaceful nuclear program. They certainly don’t need a heavy-water reactor at Arak in order to have a peaceful nuclear program. . . . And so the question ultimately is going to be, are they prepared to roll back some of the advancements that they’ve made.” The answer to his question, by now, is clear: the Iranians will not roll back anything.
The president believes that globalization and economic integration will induce Tehran to forgo its nuclear ambitions. Meanwhile Iran’s rulers are growing stronger, bolder, and ever closer to nuclear breakout capacity.
In an effort to bolster that initiative, Speaker of the House John Boehner invited Benjamin Netanyahu to Washington to address Congress on Iran. Netanyahu accepted the invitation without first consulting the White House, which reacted in a storm of indignation, describing the move as an egregious break in protocol and an insult to the president. Instead of trying to paper over the disagreement, Obama has done everything in his power to advertise it. In making his personal rift with Netanyahu the subject of intense public debate, the White House means to direct attention away from the strategic rift between them—and from the fact that the entire Israeli elite, regardless of political orientation, as well as much of the U.S. Congress, regards the president’s conciliatory approach to Iran as profoundly misguided.
Meanwhile, the president is depicting his congressional critics as irresponsible warmongers. He would have us believe that there are only two options: his undeclared détente with Iran and yet another war in the Middle East. This is a false choice. It ignores the one policy that every president since Jimmy Carter has pursued till now: vigorous containment on all fronts, not just in the nuclear arena. Obama, however, is intent on obscuring this option, and for a simple reason: an honest debate about it would force him to come clean with the American people and admit the depth of his commitment to the strategy whose grim results are multiplying by the day.
Perhaps the president is correct. Perhaps globalization will remove the roughness from the Islamic Republic just as ocean waves polish the jagged edges of shells. If so, however, it will happen on much the same, oceanic schedule. In the meantime, the seasoned thugs in Tehran whom the president has appointed as his strategic partners in a new world order grow stronger and bolder: ever closer to nuclear breakout capacity, ever more confident in their hegemonic objectives. On condition that they forgo their nuclear ambitions, the president has offered them “a path to break through [their] isolation” and become “a very successful regional power.” They, for their part, at minuscule and temporary inconvenience to themselves, have not only reaped the economic and diplomatic rewards pursuant to participation in the JPOA but also fully preserved those nuclear ambitions and the means of achieving them. Having bested the most powerful country on earth in their drive for success on their terms, they have good reason to be confident.



+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++3)
4)
"The same desire to accommodate Iran has tailored Obama’s strategy toward the terrorist group Islamic State.
That, too, has not received the attention it deserves."
"Meanwhile, the president is depicting his congressional critics as irresponsible warmongers. He would have us believe that there are only two options: his undeclared détente with Iran and yet another war in the Middle East. This is a false choice. It ignores the one policy that every president since Jimmy Carter has pursued till now: vigorous containment on all fronts, not just in the nuclear arena. Obama, however, is intent on obscuring this option, and for a simple reason: an honest debate about it would force him to come clean with the American people and admit the depth of his commitment to the strategy whose grim results are multiplying by the day.
As a matter of ideology as much as strategy, Obama believes that integrating Iran into the international diplomatic and economic system is a much more effective method of moderating its aggressive behavior than applying more pressure. Contrary to logic, and to all the accumulated evidence before and since the November 2013 interim agreement, he appears also to believe that his method is working."
Obama's Secret Iran Strategy
The president has long been criticized for his lack of strategic vision. But what if a strategy, centered on Iran, has been in place from the start and consistently followed to this day?
President Barack Obama wishes the Islamic Republic of Iran every success. Its leaders, he explained in a recent interview, stand at a crossroads. They can choose to press ahead with their nuclear program, thereby continuing to flout the will of the international community and further isolate their country; or they can accept limitations on their nuclear ambitions and enter an era of harmonious relations with the rest of the world. “They have a path to break through that isolation and they should seize it,” the president urged—because “if they do, there’s incredible talent and resources and sophistication . . . inside of Iran, and it would be a very successful regional power.”
How eager is the president to see Iran break through its isolation and become a very successful regional power? Very eager. A year ago, Benjamin Rhodes, deputy national-security adviser for strategic communication and a key member of the president’s inner circle, shared some good news with a friendly group of Democratic-party activists. The November 2013 nuclear agreement between Tehran and the “P5+1”—the five permanent members of the UN Security Council plus Germany—represented, he said, not only “the best opportunity we’ve had to resolve the Iranian [nuclear] issue,” but “probably the biggest thing President Obama will do in his second term on foreign policy.” For the administration, Rhodes emphasized, “this is healthcare . . . , just to put it in context.” Unaware that he was being recorded, he then confided to his guests that Obama was planning to keep Congress in the dark and out of the picture: “We’re already kind of thinking through, how do we structure a deal so we don’t necessarily require legislative action right away.”
Why the need to bypass Congress? Rhodes had little need to elaborate. As the president himself once noted balefully, “[T]here is hostility and suspicion toward Iran, not just among members of Congress but the American people”—and besides, “members of Congress are very attentive to what Israel says on its security issues.” And that “hostility and suspicion” still persist, prompting the president in his latest State of the Union address to repeat his oft-stated warning that he will veto “any new sanctions bill that threatens to undo [the] progress” made so far toward a “comprehensive agreement” with the Islamic Republic.
As far as the president is concerned, the less we know about his Iran plans, the better. Yet those plans, as Rhodes stressed, are not a minor or incidental component of his foreign policy. To the contrary, they are central to his administration’s strategic thinking about the role of the United States in the world, and especially in the Middle East.
Moreover, that has been true from the beginning. In the first year of Obama’s first term, a senior administration official would later tell David Sanger of the New York Times,
“There were more [White House] meetings on Iran than there were on Iraq, Afghanistan, and China. It was the thing we spent the most time on and talked about the least in public [emphasis added].” All along, Obama has regarded his hoped-for “comprehensive agreement” with Iran as an urgent priority, and, with rare exceptions, has consistently wrapped his approach to that priority in exceptional layers of secrecy.
“There were more [White House] meetings on Iran than there were on Iraq, Afghanistan, and China. It was the thing we spent the most time on and talked about the least in public [emphasis added].” All along, Obama has regarded his hoped-for “comprehensive agreement” with Iran as an urgent priority, and, with rare exceptions, has consistently wrapped his approach to that priority in exceptional layers of secrecy.
From time to time, critics and even friends of the president have complained vocally about the seeming disarray or fecklessness of the administration’s handling of foreign policy. Words like amateurish, immature, and incompetent are bandied about; what’s needed, we’re told, is less ad-hoc fumbling, more of a guiding strategic vision. Most recently, Leslie Gelb, a former government official and past president of the Council on Foreign Relations, has charged that “the Obama team lacks the basic instincts and judgment necessary to conduct U.S. national-security policy,” and has urged the president to replace the entire inner core of his advisers with “strong and strategic people of proven . . . experience.”
One sympathizes with Gelb’s sense of alarm, but his premises are mistaken. Inexperience is a problem in this administration, but there is no lack of strategic vision. Quite the contrary: a strategy has been in place from the start, and however clumsily it may on occasion have been implemented, and whatever resistance it has generated abroad or at home, Obama has doggedly adhered to the policies that have flowed from it.
In what follows, we’ll trace the course of the most important of those policies and their contribution to the president’s announced determination to encourage and augment Iran’s potential as a successful regional power and as a friend and partner to the United States.
2009-2010: Round One, Part I
In the giddy aftermath of Obama’s electoral victory in 2008, anything seemed possible. The president saw himself as a transformational leader, not just in domestic politics but also in the international arena, where, as he believed, he had been elected to reverse the legacy of his predecessor, George W. Bush. To say that Obama regarded Bush’s foreign policy as anachronistic is an understatement. To him it was a caricature of yesteryear, the foreign-policy equivalent of Leave It to Beaver. Obama’s mission was to guide America out of Bushland, an arena in which the United States assembled global military coalitions to defeat enemies whom it depicted in terms like “Axis of Evil,” and into Obamaworld, a place more attuned to the nuances, complexities, and contradictions—and opportunities—of the 21st century. In today’s globalized environment, Obama told the United Nations General Assembly in September 2009, “our destiny is shared, power is no longer a zero-sum game. No one nation can or should try to dominate another nation. . . . No balance of power among nations will hold.”
If, in Bushland, America had behaved like a sheriff, assembling a posse to go in search of monsters, in Obamaworld America would disarm its rivals by ensnaring them in a web of cooperation.
For the new president, nothing revealed the conceptual inadequacies of Bushland more clearly than the 2003 invasion of Iraq. Before coming to Washington, Obama had opposed the toppling of the Iraqi dictator Saddam Hussein; once in the U.S. Senate, he rejected Bush’s “surge” and introduced legislation to end the war. Shortly after his inauguration in January 2009, he pledged to bring the troops home quickly—a commitment that he would indeed honor. But if calling for withdrawal from Iraq had been a relatively easy position to take for a senator, for a president it raised a key practical question: beyond abstract nostrums like “no nation can . . . dominate another nation,” what new order should replace the American-led system that Bush had been building?
This was, and remains, the fundamental strategic question that Obama has faced in the Middle East, though one would search his speeches in vain for an answer to it. But Obama does have a relatively concrete vision. When he arrived in Washington in 2006, he absorbed a set of ideas that had incubated on Capitol Hill during the previous three years—ideas that had received widespread attention thanks to the final report of the Iraq Study Group, a bipartisan congressional commission whose co-chairs, former secretary of state James Baker and former Indiana congressman Lee Hamilton, interpreted their mission broadly, offering advice on all key aspects of Middle East policy.
The report, published in December 2006, urged then-President Bush to take four major steps: withdraw American troops from Iraq; surge American troops in Afghanistan; reinvigorate the Arab-Israeli “peace process”; and, last but far from least, launch a diplomatic engagement of the Islamic Republic of Iran and its junior partner, the Assad regime in Syria. Baker and Hamilton believed that Bush stood in thrall to Israel and was therefore insufficiently alive to the benefits of cooperating with Iran and Syria. Those two regimes, supposedly, shared with Washington the twin goals of stabilizing Iraq and defeating al-Qaeda and other Sunni jihadi groups. In turn, this shared interest would provide a foundation for building a concert system of states—a club of stable powers that could work together to contain the worst pathologies of the Middle East and lead the way to a sunnier future.
Expressing the ethos of an influential segment of the foreign-policy elite, the Baker-Hamilton report became the blueprint for the foreign policy of the Obama administration, and its spirit continues to pervade Obama’s inner circle. Denis McDonough, now the president’s chief of staff, once worked as an aide to Lee Hamilton; so did Benjamin Rhodes, who helped write the Iraq Study Group’s report. Obama not only adopted the blueprint but took it one step further, recruiting Vladimir Putin’s Russia as another candidate for membership in the new club. The administration’s early “reset” with Russia and its policy of reaching out to Iran and Syria formed two parts of a single vision. If, in Bushland, America had behaved like a sheriff, assembling a posse (“a coalition of the willing”) to go in search of monsters, in Obamaworld America would disarm its rivals by ensnaring them in a web of cooperation. To rid the world of rogues and tyrants, one must embrace and soften them.

Lee Hamilton, George W. Bush, and James Baker during a meeting of the Iraq Study Group, Wednesday, Dec. 6. 2006. White House Photo.
How would this work in the case of Iran? During the Bush years, an elaborate myth had developed according to which the mullahs in Tehran had themselves reached out in friendship to Washington, offering a “grand bargain”: a deal on everything from regional security to nuclear weapons. The swaggering Bush, however, had slapped away the outstretched Iranian hand, squandering the opportunity of a lifetime to normalize U.S.-Iranian relations and thereby bring order to the entire Middle East.
Obama based his policy of outreach to Tehran on two key assumptions of the grand-bargain myth: that Tehran and Washington were natural allies, and that Washington itself was the primary cause of the enmity between the two. If only the United States were to adopt a less belligerent posture, so the thinking went, Iran would reciprocate. In his very first television interview from the White House, Obama announced his desire to talk to the Iranians, to see “where there are potential avenues for progress.” Echoing his inaugural address, he said, “[I]f countries like Iran are willing to unclench their fist, they will find an extended hand from us.”
Unfortunately, the Supreme Leader of Iran, Ali Khamenei, ignored the president’s invitation. Five months later, in June 2009, when the Green Movement was born, his autocratic fist was still clenched. As the streets of Tehran exploded in the largest anti-government demonstrations the country had seen since the revolution of 1979, he used that fist to beat down the protesters. For their part, the protesters, hungry for democratic reform and enraged by government rigging of the recent presidential election, appealed to Obama for help. He responded meekly, issuing tepid statements of support while maintaining a steady posture of neutrality. To alienate Khamenei, after all, might kill the dream of a new era in U.S.-Iranian relations.
If this show of deference was calculated to warm the dictator’s heart, it failed. “What we intended as caution,” one of Obama’s aides would later tell a reporter, “the Iranians saw as weakness.” Indeed, the president’s studied “caution” may even have emboldened Tehran to push forward, in yet another in the long series of blatant violations of its obligations under the nuclear Nonproliferation Treaty (NPT), with its construction of a secret uranium enrichment facility in an underground bunker at Fordow, near Qom.
When members of Iran’s Green Movement appealed to Obama for help in 2009, he responded meekly—after all, to alienate Khamenei might kill the dream of a new era in U.S.-Iranian relations.
This time, Obama reacted. Revealing the bunker’s existence, he placed Khamenei in a tough spot. The Russians, who had been habitually more lenient toward the Iranian nuclear program than the Americans, were irritated by the disclosure of this clandestine activity; the French were moved to demand a strong Western response.
But when Khamenei finessed the situation by adopting a seemingly more flexible attitude toward negotiations, Obama quickly obliged. Delighted to find a receptive Iranian across the table, he dismissed the French call for toughness, instead volunteering a plan that would meet Iran’s desire to keep most of its nuclear infrastructure intact while proving to the world that it was not stockpiling fissile material for a bomb. In keeping with his larger aspirations, the president also placed Moscow at the center of the action, proposing that the Iranians transfer their enriched uranium to Russia in exchange for fuel rods capable of powering a nuclear reactor but not of being used in a bomb. The Iranian negotiators, displaying their new spirit of compromise, accepted the terms. Even President Ahmadinejad, the notorious hardliner, pronounced himself on board.
Obama, it seemed to some, had pulled off a major coup. Less than a year after taking office, he was turning his vision of a new Middle East order into a reality. Or was he? Once the heat was off, Khamenei reneged on the deal, throwing the president back to square one and in the process weakening him politically at home, where congressional skeptics of his engagement policy now began lobbying for more stringent economic sanctions on Tehran. To protect his flank, Obama tacked rightward, appropriating, if with visible reluctance, some of his opponents’ rhetoric and bits of their playbook as well. In 2010, he signed into law the Comprehensive Iran Sanctions, Accountability, and Divestment Act (CISADA), which eventually would prove more painful to Iran than any previous measure of its kind.
In later years, whenever Obama would stand accused of being soft on Iran, he would invariably point to CISADA as evidence to the contrary. “[O]ver the course of several years,” he stated in March 2014, “we were able to enforce an unprecedented sanctions regime that so crippled the Iranian economy that they were willing to come to the table.” The “table” in question was the negotiation resulting in the November 2013 agreement, known as the Joint Plan of Action (JPOA), which we shall come to in due course. But masked in the president’s boast was the fact that he had actually opposed CISADA, which was rammed down his throat by a Senate vote of 99 to zero.
Once the bill became law, a cadre of talented and dedicated professionals in the Treasury Department set to work implementing it. But the moment of presumed “convergence” between Obama and his congressional skeptics proved temporary and tactical; their fundamental difference in outlook would become much more apparent in the president’s second term. For the skeptics, the way to change Khamenei’s behavior was to place him before a stark choice: dismantle Iran’s nuclear program—period—or face catastrophic consequences. For Obama, to force a confrontation with Khamenei would destroy any chance of reaching an accommodation on the nuclear front and put paid to his grand vision of a new Middle East order.
2011-2012: Round One, Part II
“The hardest cross I have to bear is the Cross of Lorraine,” Winston Churchill supposedly cracked about managing his wartime relations with Charles de Gaulle. As Obama sees it, his hardest cross to bear has been the Star of David, represented by Israel’s prime minister Benjamin Netanyahu.
To the Israelis, who have long regarded Iran’s nuclear program as an existential threat, Obama’s engagement policy was misguided from the start. Their assessment mattered, because influential Americans listened to them. What was more, American Jews constituted an important segment of the Democratic party’s popular base and an even more important segment of its donors. In the election year of 2012, for Obama to be perceived as indifferent to Israeli security would jeopardize his prospects of a second term—and hardly among Jews alone.
When the Israelis threatened to attack Iran, Obama responded by putting Israel in a bear hug. From one angle, it looked like an expression of friendship. From another, like an effort to break Netanyahu’s ribs.
The Israelis did more than just criticize Obama; they also threatened to take action against Iran that would place the president in an intolerable dilemma. In 2011, Ehud Barak, the defense minister at the time, announced that Iran was quickly approaching a “zone of immunity,” meaning that its nuclear program would henceforth be impervious to Israeli attack. As Iran approached that zone, Israel would have no choice but to strike. And what would America do then? The Israeli warnings grew ever starker as the presidential election season heated up. Netanyahu, it seemed, was using the threat of Israeli action as a way of prodding Washington itself to take a harder line.
To this challenge, Obama responded by putting Israel in a bear hug. From one angle, it looked like an expression of profound friendship: the president significantly increased military and intelligence cooperation, and he insisted, fervently and loudly, that his policy was to prevent Iran from acquiring a nuclear weapon by all means possible. With the aid of influential American Jews and Israelis who testified to his sincerity, Obama successfully blunted the force of the charge that he was hostile to Israel.
From another angle, however, the bear hug looked like an effort to break Netanyahu’s ribs. Even while expressing affection for Israel, Obama found ways to signal his loathing for its prime minister. During one tense meeting at the White House, for example, the president abruptly broke off to join his family for dinner, leaving Netanyahu to wait for him alone. In mitigation, Obama supporters would adduce ongoing friction between the two countries over West Bank settlements and peace negotiations with the Palestinians. This was true enough, but the two men differed on quite a number of issues, among which Iran held by far the greatest strategic significance. In managing the anxieties of his liberal Jewish supporters, Obama found it useful to explain the bad atmosphere as a function of Netanyahu’s “extremism” rather than of his own outreach to Iran—to suggest, in effect, that if only the hothead in the room would sit down and shut up, the grownups could proceed to resolve the Iranian nuclear problem along reasonable lines.
The tactic proved effective. At least for the duration, Obama prevented Israel from attacking Iran; preserved American freedom of action with regard to Iran’s nuclear program; and kept his disagreements with the Israeli government within the comfort zone of American Jewish Democrats.
Sign Up For Our E-Mail List Get the latest from Mosaic right in your inbox
If, however, Netanyahu was Obama’s biggest regional headache, there was no lack of others. King Abdullah of Saudi Arabia was certainly the most consequential. Obama had assumed that the king would welcome his approach to the Middle East as a breath of fresh air. After all, the Baker-Hamilton crowd regarded the Arab-Israeli conflict as the major irritant in relations between the United States and the Arabs. Bush’s close alignment with Israel, so the thinking went, had damaged those relations; by contrast, Obama, the moment he took office, announced his goal of solving the Arab-Israeli conflict once and for all, and followed up by picking a fight with Netanyahu over Jewish settlements in the West Bank. How could the Saudis react with anything but pleasure?
In fact, they distanced themselves—bluntly and publicly. While meeting with Secretary of State Hillary Clinton at the end of July 2009, Saudi Foreign Minister Saud al-Faisal announced that Obama’s approach to solving the Arab-Israeli conflict “has not and, we believe, will not lead to peace.” Behind that statement lay a complex of attitudes toward the Israeli-Palestinian conflict itself, but much more than that. At the end of the Bush administration, King Abdullah had made his top regional priority abundantly clear when, according to leaked State Department documents, he repeatedly urged the United States to destroy Iran’s nuclear program and thereby “cut off the head of the snake” in the Middle East.
When Obama strode into office and announced his desire to kiss the snake, the Saudis lost no time in making their displeasure felt. Three months later, the king responded gruffly to an extensive presentation on Obama’s outreach program by Dennis Ross, then a senior official in the State Department with responsibility for Iran. “I am a man of action,” Abdullah said according to a New York Times report. “Unlike you, I prefer not to talk a lot.” He then posed a series of pointed questions that Ross could not answer. “What is your goal? What will you do if this does not work? What will you do if the Chinese and the Russians are not with you? How will you deal with Iran’s nuclear program if there is not a united response?” The questions added up to a simple point: your Iran policy is based on wishful thinking.
As it happens, one traditional American ally in the region was—at least at first—untroubled by Obama’s policy of Iran engagement: the Turkish leader Recep Tayyip Erdoğan. Indeed, Erdoğan found much to extol in the new American initiative, which dovetailed perfectly with his own foreign policy of “zero problems with [Arab and Muslim] neighbors.” Among other things, Erdoğan meant to establish Ankara as the middleman between the United States and Iran and Syria, Turkey’s traditional adversaries. This vision nested so comfortably within Obama’s planned concert system that Erdoğan quickly became one of the few international personalities with whom Obama developed a close personal rapport.
Contrary to what observers have long assumed, Obama does connect his Iran policy and his Syria policy: just as he showed deference to Iran on the nuclear front, he has deferred to the Iranian interest in Syria.
Soon, however, serious tensions arose. By the summer of 2012, one problem overshadowed all others: Syria—and behind Syria, Iran. Erdoğan watched in horror as the Iranians together with their proxies, Hizballah and Iraqi Shiite militias, intervened in the Syrian civil war. Iranian-directed units were not only training and equipping Bashar Assad’s forces in his battle for survival, but also engaging in direct combat. At the same time, within the Syrian opposition to Assad, a radical Sunni jihadi element was growing at an alarming rate. In short order, the Turks were adding their voice to a powerful chorus—including Saudi Arabia, the Gulf sheikhdoms, and the Jordanians—urgently requesting that Washington take action to build up the moderate Sunni opposition to both Assad and Iran.
The director of the CIA, David Petraeus, responded to this request by America’s regional allies with a plan to train and equip Syrian rebels in Jordan and to assist them once back in Syria. Defense Secretary Leon Panetta, Secretary of State Hillary Clinton, and General Martin Dempsey, the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, all supported the Petraeus plan. But Obama rejected it.
Why? Undoubtedly the president had a mix of reasons and possible motives, which were the objects of extensive speculation in the media. But one motive was never included in the list: namely, his fear of antagonizing Iran. For the longest time, it was simply assumed that Obama drew no connection between his Iran policy and his Syria policy. This, however, was not the case. In fact—as we shall see below—just as, from the beginning, he showed deference to Iran on the nuclear front, he showed the same deference to the Iranian interest in Syria.

Islamic State fighters in Aleppo, Syria on July 4, 2013. Photo by Daniel Leal-Olivas/Corbis.
2013-2014: Round Two, The Secret Backchannel
An ostensible thaw in American-Iranian relations occurred early in the president’s second term. To hear him tell it today, what precipitated the thaw was a strategic shift by Tehran on the nuclear front. In his version of the story—let’s call it the “official version”—two factors account for the Iranian change of heart. One of them was American coercive diplomacy; the other was a new spirit of reform in Tehran. And the two were interrelated. The first, as Obama himself explained in the March 2014 interview cited earlier, had taken the form of “an unprecedented sanctions regime that so crippled the Iranian economy that [the Iranians] were willing to come to the table.” The second was a corollary of the first. The same sanctions regime had also helped bring to power the new government of Hassan Rouhani, whose moderate approach would in turn culminate in the November 2013 signing of the interim nuclear deal, which “for the first time in a decade halts their nuclear program.”
Obama’s version is an after-the-fact cocktail of misdirection and half-truths, stirred by him and his aides and served up with a clear goal in mind: to conceal Round Two of his Iran outreach.
The turning point in the American-Iranian relationship was not, as the official version would have it, the election of Hassan Rouhani in June 2013. It was the reelection of Barack Obama in November 2012.
In early 2013, at the outset of his second term, Obama developed a secret bilateral channel to Ahmadinejad’s regime. When the full impact of this is taken into account, a surprising fact comes to light. The turning point in the American-Iranian relationship was not, as the official version would have it, the election of Hassan Rouhani in June 2013. It was the reelection of Barack Obama in November 2012.
Indeed, the first secret meeting with the Iranians (that is, the first we know of) took place even earlier, in early July 2012, eleven months before Rouhani came to power. Jake Sullivan, who at the time was the director of policy planning in Hillary Clinton’s State Department, traveled secretly to Oman to meet with Iranian officials. The Obama administration has told us next to nothing about Sullivan’s meeting, so we are forced to speculate about the message that he delivered.
Most pertinent is the timing. At that moment, pressure was mounting on the president to intervene in Syria. Sullivan probably briefed the Iranians on Obama’s strong desire to stay out of that conflict, and may have sought Tehran’s help in moderating Assad’s behavior. But summer 2012 was also the height of the American presidential campaign. Perhaps Sullivan told the Iranians that the president was keen to restart serious nuclear negotiations after the election. Recall that this meeting took place shortly after a hot microphone had caught Obama saying to Dmitry Medvedev, the Russian president, “On all these issues, but particularly missile defense, this can be solved, but it’s important . . . to give me space. This is my last election. After my election, I have more flexibility.”
Did Sullivan give the Iranians a similar message? Did he tell Ahmadinejad’s officials that Obama’s need to secure the pro-Israel vote had forced him to take a deceptively belligerent line toward Iran? That Iran had nothing to fear from an Israeli attack? That after the election Obama would demonstrate even greater flexibility on the nuclear issue?
Whatever the answers to these questions, it is a matter of record that Obama opened his second term with a campaign of outreach to Tehran—a campaign that was as intensive as it was secret. By February 2013, a month after his inauguration, the backchannel was crowded with American officials. Not just Sullivan, but Deputy Secretary of State William Burns, National Security Council staffer Puneet Talwar, State Department non-proliferation adviser Robert Einhorn, and Ambassador to the United Nations Susan Rice were all engaging their Iranian counterparts.
According to the official version, this stampede toward Tehran had no impact on Iranian-American relations. Nothing notable occurred in that realm, we are told, until the arrival on the scene of Rouhani. In fact, however, it was during this earlier period that Obama laid the basis for the November 2013 Joint Plan of Action. And that agreement was the product of three American concessions—two of which, and possibly the third as well, were made long before Rouhani ever came to power.
In April 2013, the Americans and their P5+1 partners met with Iranian negotiators in Almaty, Kazakhstan, where they offered to relieve the sanctions regime in exchange for the elimination of Iran’s stockpiles of uranium that had already been enriched to 20 percent. This was concession number one, bowing to the longstanding Iranian demand for economic compensation immediately, before a final agreement could be reached. Even more important was concession number two, which permitted the Iranians to continue enriching uranium to levels of 5 percent—this, despite the fact that six United Nations Security Council resolutions had ordered Iran to cease all enrichment and reprocessing activities.
Iranian negotiators rejected these two gifts—or, rather, they pocketed them and demanded a third, the one they coveted the most. Hailing the proposals by their counterparts as a step in the right direction, they criticized them for failing to stipulate the Iranian “right to enrich.” There was a difference, they argued, between temporarily permitting Iran to enrich uranium to 5 percent and recognizing its inalienable right to do so. If Obama wanted a deal, he would have to agree to shred the Security Council resolutions by offering, up front, an arrangement that would end the economic sanctions on Iran entirely and that would allow the Iranians to enrich uranium in perpetuity.
By exaggerating the spirit of reform in Tehran, the White House was able to suggest that Iran, and not America, had compromised.
Obama’s acceptance of this condition, the third and most important American gift, is what made the Joint Plan of Action possible. The American negotiators transmitted the president’s acceptance to the Iranians in the backchannel, and then John Kerry sprang it on his hapless negotiating partners in November. We do not know when, precisely, Obama made this offer, but the Iranians set their three conditions before Rouhani took office.
In brief, the Iranian election was hardly the key factor that made the interim deal possible. But it did supply window dressing at home when it came to selling the deal to Congress and the American public. By exaggerating the spirit of reform in Tehran, the White House was able to suggest that Rouhani’s embrace of the deal represented an Iranian, not an American, compromise. In truth, Obama neither coerced nor manipulated; he capitulated, and he acquiesced.
Round Two: Iran, Syria, and Islamic State
The nuclear issue wasn’t the only tender spot in U.S.-Iran relations in this period. Before returning to it, let’s look briefly at two other regional fronts.
Obama’s second term has also included efforts to accommodate Iran over Syria. Susan Rice, by now the president’s national-security adviser, inadvertently admitted as much in an address she delivered on September 9, 2013, a few weeks after Bashar Assad had conducted a sarin-gas attack on Ghouta, a suburb outside Damascus, that killed approximately 1,500 civilians. Reviewing past American efforts to restrain the Syrian dictator, Rice blithely depicted Tehran as Washington’s partner. “At our urging, over months, Russia and Iran repeatedly reinforced our warning to Assad,” she explained. “We all sent the same message again and again: don’t do it.”
Why did Obama back off on strikes against Syria? Could it have been fear of scuttling the biggest—and still secret—foreign-policy initiative of his entire presidency?
Rice’s remarks were disingenuous. In reality, the Islamic Republic was then precisely what it remains today, namely, the prime enabler of Assad’s murder machine. But Rice’s intention was not to describe Iranian behavior accurately. In addition to accustoming the American press and foreign-policy elite to the idea that Iran was at least a potential partner, her speech was aimed at influencing Congress’s deliberation of air strikes against Syria—strikes that Obama had abruptly delayed a week and a half earlier in what will certainly be remembered as one of the oddest moments of his presidency.
The oddity began shortly after Obama sent Secretary of State John Kerry out to deliver a Churchillian exhortation on the theme of an impending American attack. While that speech was still reverberating, the president convened a meeting of his inner circle in the Oval Office, where he expressed misgivings about the policy that his Secretary of State had just announced. Curiously, the meeting did not include either Kerry or Secretary of Defense Chuck Hagel, the principal members of his senior national-security staff. Obama then invited Denis McDonough to break away from the others and join him for a private walk around the White House grounds. On his return, Obama stunned the waiting group with the news that he had decided to delay the strikes on Assad in order to seek congressional approval.
What thoughts did Obama share with McDonough? We can dispense with the official explanation, which stresses the president’s principled belief in the need to consult the legislative branch on matters of war and peace. That belief had played no part in previous decisions, like the one to intervene in Libya. Clearly, Obama was hiding behind Congress in order either to delay action or to kill it altogether. The true reasons for the delay were evidently too sensitive even for the ears of his closest national-security aides. Could they have included fear of scuttling the biggest—and still secret—foreign-policy initiative of his second term, possibly of his entire presidency?
In the event, the punt to Congress bought Obama some time, but at a significant political cost. At home the decision made him appear dithering and weak; on Capitol Hill, Democrats quietly fumed over the way the White House was abruptly ordering them out on a limb. In Syria, Assad crowed with delight as his opponents crumpled in despair. Elsewhere, American allies felt exposed and vulnerable, wondering whether Obama would ever truly come to their aid in a pinch.
As we know, Obama’s quandary would become Moscow’s opportunity. Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov offered the president a way to regain his balance. Russia and the United States, Lavrov proposed, would cooperate to strip Assad of his sarin gas. From the sidelines, the Iranians publicly applauded the proposal, and Obama jumped to accept it.
But the deal was a quid pro quo. In return for a minor (though highly visible) concession from Assad, Obama tacitly agreed not to enter the Syrian battlefield. In effect, the Russians, Assad, and the Iranians were offering him, and he was accepting, surrender with honor, enabling him to say later, with a straight face, that the episode was a successful example of his coercive diplomacy. “Let’s be very clear about what happened,” he bragged in his March 2014 interview. “I threatened [sic] kinetic strikes on Syria unless they got rid of their chemical weapons.” In reality, Assad only gained—and gained big. Obama immediately muted his calls for Assad to step down from power, and his behavior thoroughly demoralized the Syrian opposition. Nor did the deal stop Assad from launching further chemical attacks. Once deprived of his sarin stockpiles, he simply switched to chlorine.
During an interview on primetime television shortly after Lavrov offered his country’s help, Obama pointed to Russian and Iranian cooperation with Washington as one of the bargain’s greatest benefits. The “good news,” he said, “is that Assad’s allies, both Russia and Iran, recognize that this [use of sarin] was—this was a breach, that this was a problem. And for them to potentially put pressure on Assad to say, ‘Let’s figure out a way that the international community gets control of . . . these weapons in a verifiable and forcible way’—I think it’s something that we will run to ground.”
This was fictive. Obama made it sound as if Tehran was eager to punish Assad for his use of chemical weapons, but nothing could have been farther from the truth. Even as he was speaking, Iran was publicly blaming the Syrian rebels, not Assad, for the Ghouta attack. Nor was stopping the slaughter ever the president’s true goal. From his perspective, he did not have the power to prevent Assad’s atrocities. He did, however, have the sense to recognize a good thing when he saw it. The opportunity to join with Iran in an ostensibly cooperative venture was too good to let slip away—and so he seized it.
That Obama has treated Syria as an Iranian sphere of interest all along has been brought home in a recent report in the Wall Street Journal. In August 2014, according to the Journal, the president wrote a letter to Ali Khamenei, acknowledging the obstacle to their cooperation presented by the nuclear impasse but taking pains to reassure Khamenei regarding the fate of Assad, his closest ally. American military operations inside Syria, he wrote, would target neither the Syrian dictator nor his forces.
This element of the president’s thinking has received remarkably little attention, even though Obama himself pointed to it directly in a January 2014 interview with David Remnick, the editor of theNew Yorker. The Arab states and Israel, Obama said then, wanted Washington to be their proxy in the contest with Iran; but he adamantly refused to play that role. Instead, he envisioned, in Remnick’s words, “a new geostrategic equilibrium, one less turbulent than the current landscape of civil war, terror, and sectarian battle.” Who would help him develop the strategy to achieve this equilibrium? “I don’t really even need George Kennan right now,” the president responded, alluding to the acknowledged godfather of the cold-war strategy of containment. What he truly needed instead were strategic partners, and a prime candidate for that role was—he explained—Iran.
Obama was here revealing his main rationale in 2012 for rejecting the Petraeus plan to arm the Syrian opposition that we examined earlier. Clearly, the president viewed the anti-Assad movement in Syria just as he had viewed the Green Movement in Iran three years earlier: as an impediment to realizing the strategic priority of guiding Iran to the path of success. Was the Middle East in fact polarized between the Iranian-led alliance and just about everyone else? Yes. Were all traditional allies of the United States calling for him to stand up to Iran? Yes. Did the principal members of his National Security Council recommend as one that the United States heed the call of the allies? Again, yes. But Obama’s eyes were still locked on the main prize: the grand bargain with Tehran.

Iranian President Hassan Rouhani, left, talks to his Foreign Minister Mohammad Javad Zarif at Davos in 2014. AP Photo/Michel Euler.
The same desire to accommodate Iran has tailored Obama’s strategy toward the terrorist group Islamic State. That, too, has not received the attention it deserves.
Last June, when Islamic State warriors captured Mosul in northern Iraq, the foreign-policy approval ratings of the president plummeted, and Obama’s critics claimed, not for the first time, that he had no strategy at all. Ben Rhodes sprang to his defense, suggesting that despite appearances to the contrary, the administration actually had a plan, if a hitherto unannounced one. “We have longer-run plays that we’re running,” he said. “Part of this is keeping your eye on the long game even as you go through tumultuous periods.”
The administration has subtly exploited the rise of the Islamic State to elevate Obama’s outreach to Iran. Behind the scenes, coordination and consultation have reached new heights.
Rhodes offered no details, and subsequent events seemed to confirm the impression that Obama actually had no long game. In addition to being caught flat-footed by Islamic State, moreover, he was reversing himself on other major issues: sending troops back to Iraq after having celebrated their homecoming, ordering military operations in Syria that he had opposed for years. How could such reversals be consistent with a long game?
The answer is that the reversals, although real, involved much less than met the eye, and the long game remained in place. In August, it seemed as if the American military was preparing to mount a sustained intervention in both Iraq and Syria; today, however, it is increasingly apparent that Obama has at best a semi-coherent containment plan for Iraq and no plan at all for Syria—a deficiency that was obvious from the start. At a hearing of the Senate Foreign Relations committee, Senator Marco Rubio pointed to the obvious weaknesses in the administration’s approach, and asked John Kerry how to fix them. Kerry stunningly suggested that the gaps would be filled by . . . Iran and Assad. “[Y]ou’re presuming that Iran and Syria don’t have any capacity to take on” Islamic State, Kerry said. “If we are failing and failing miserably, who knows what choice they might make.”
Here, giving the game away, Kerry provided a glimpse at the mental map of the president and his top advisers. The administration has indeed subtly exploited the rise of terrorist enclaves to elevate Obama’s outreach to Iran. Behind the scenes, coordination and consultation have reached new heights.
Meanwhile, so have expressions of dissatisfaction with traditional allies for taking positions hostile to Iran. Our “biggest problem” in Syria is our own regional allies, Vice President Joseph Biden complained to students at Harvard University in early October. Turkey, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates were “so determined to take down Assad” that they were pouring “hundreds of millions of dollars and tens of thousands of tons of weapons” into the Syrian opposition. A few weeks later, a senior Obama administration official cuttingly described another ally, Israel’s prime minister, as “a chickenshit,” and a second official, similarly on the record, bragged about the success of the United States in shielding the Islamic Republic from Israel. “[U]ltimately [Netanyahu] couldn’t bring himself to pull the trigger. It was a combination of our pressure and his own unwillingness to do anything dramatic. Now it’s too late.”
Of course, administration officials routinely insist that the United States is not working with Tehran. The coordination, however, is impossible to disguise. Thus, when Iranian jets recently appeared in Iraqi skies, they professed ignorance. Reporters, noting that the jets were flying sorties in the same air space as American jets and striking related targets, asked the Pentagon spokesman how the American and Iranian air forces could work in the same space without colliding. “We are flying missions over Iraq, [and] we coordinate with the Iraqi government as we conduct those,” said the spokesman. “It’s up to the Iraqi government to de-conflict that airspace.” When Kerry was asked about the news that the Iranian air force was operating in Iraq, he responded that this was a “net positive.”
A positive? With American acquiescence, Iran is steadily taking control of the security sector of the Iraqi state. Soon it will dominate the energy sector as well, giving it effective control over the fifth largest oil reserves in the world. When the announced goal of the United States is to build up a moderate Sunni bloc capable of driving a wedge between Islamic State and the Sunni communities, aligning with Iran is politically self-defeating. In both Iraq and Syria, Iran projects its power through sectarian militias that slaughter Sunni Muslims with abandon. Are there any Sunni powers in the region that see American outreach to Tehran as a good thing? Are there any military-aged Sunni men in Iraq and Syria who now see the United States as a friendly power? There are none.
In theory, one might argue that although an association with Iran is politically toxic and militarily dangerous, the capabilities it brings to the fight against the Islamic State more than compensate. But they don’t. Over the last three years, Obama has given Iran a free hand in Syria and Iraq, on the simplistic assumption that Tehran would combat al-Qaeda and like-minded groups in a manner serving American interests. The result, in both countries, has been the near-total alienation of all Sunnis and the development of an extremist safe haven that now stretches from the outskirts of Baghdad all the way to Damascus. America is now applying to the disease a larger dose of the snake oil that helped cause the malady in the first place.
The approach is detrimental to American interests in other arenas as well. We received a portent of things to come on January 18 of this year, when the Israel Defense Forces struck a convoy of senior Hizballah and Iranian officers, including a general in the Revolutionary Guards, in the Golan Heights. Ten days later, Hizballah and Iran retaliated. In other words, by treating Syria as an Iranian sphere of interest, Obama is allowing the shock troops of Iran to dig in on the border of Israel—not to mention the border of Jordan. The president’s policy assumes that Israel and America’s other allies will hang back quietly while Iran takes southern Syria firmly in its grip. They will not; to assume otherwise is folly.
Round Three: 2015-
In November 2013, when Obama purchased the participation of Iran in the Joint Plan of Action, he established a basic asymmetry that has remained a key feature of the negotiations ever since. He traded permanent American concessions for Iranian gestures of temporary restraint.
The most significant such gestures by Iran were to dilute its stockpiles of uranium enriched to 20 percent; to refrain from installing new centrifuges; and to place a hold on further construction of the Arak plutonium reactor. All three, however, can be easily reversed. By contrast, the Americans recognized the Iranian right to enrich and agreed to the principle that all restrictions on Iran’s program would be of a limited character and for a defined period of time. These two concessions are major, and because they are not just the policy of the United States government but now the collective position of the permanent members of the United Nations Security Council and Germany, they will likely never be reversed.
In his negotiations with Iran, the president has traded major American concessions for Iranian gestures of temporary restraint. These concessions will likely never be reversed.
Obama has repeatedly stated, most recently in his 2015 State of the Union address, that the interim agreement “halted” the Iranian nuclear program. Or, as he put it in his March 2014 interview, the “logic” of the JPOA was “to freeze the situation for a certain period of time to allow the negotiators to work.” But the agreement froze only American actions; it hardly stopped the Iranians from moving forward.
For one thing, the JPOA restricts the program only with respect to enrichment capacity and stockpiles; it is entirely silent about the military components: ballistic missiles, procurement, warhead production. For another, to call what the JPOA achieved even in these limited domains “a freeze” is a gross exaggeration. Iranian nuclear scientists have continued to perfect their craft. They are learning how to operate old centrifuges with greater efficiency. And thanks to a loophole in the JPOA permitting work on “research and development,” they are also mastering the use of new, more effective centrifuges.
Therefore, the Iranian nuclear program is poised to surge ahead. The moment the JPOA lapses—a date first scheduled for July 2014, then rescheduled to November 2014, then re-rescheduled to June 30 of this year, possibly to be re-re-rescheduled yet again—Iran will be in a stronger position than before the negotiations began. This fact gives Tehran considerable leverage over Washington during the next rounds.
We can say with certainty that Obama has had no illusions about this asymmetry—that he conducted the negotiations with his eyes wide open—because the White House took pains to hide the truth from the American public. In 2013, instead of publishing the text of the JPOA, it issued a highly misleading fact sheet. Peppered with terms like “halt,” “roll back,” and “dismantle,” the document left the impression that the Iranians had agreed to destroy their nuclear program.
The Iranian foreign minister, however, refused to play along. He protested—loudly and publicly. “The White House version both underplays the [American] concessions and overplays Iranian commitments,” Javad Zarif correctly told a television interviewer. “The White House tries to portray it as basically a dismantling of Iran’s nuclear program. That is the word they use time and again.” He defied the interviewer to “find a . . . single word that even closely resembles dismantling or could be defined as dismantling in the entire text.”
President Rouhani went even further. In an interview with CNN’s Fareed Zakaria, he emphasized not just that Iran had refused to destroy centrifuges within the terms of the JPOA, but that it would never destroy them “under any circumstances.” Currently Iran has approximately 9,000 centrifuges installed and spinning, and roughly 10,000 more installed but inactive. Until Rouhani made his statement, the Obama administration had led journalists to believe that the final agreement would force the Iranians to dismantle some 15,000 centrifuges.Rouhani disabused the world of those expectations.
“This strikes me as a train wreck,” a distraught Zakaria exclaimed after the interview. “This strikes me as potentially a huge obstacle because the Iranian conception of what the deal is going to look like and the American conception now look like they are miles apart.” Not long thereafter, as if to confirm the point, Ali Khamenei called for an outcome that will permit the development of an industrial-sized nuclear program over the next decade.

Former Iranian President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad visits a uranium enrichment facility in Natanz, Iran, in 2008. Office of the Presidency of the Islamic Republic of Iran.
Khamenei’s hard line no doubt came as a surprise to Obama. When the president first approved the JPOA, he failed to recognize a key fact: his twin goals of liberating Iran from its international isolation and stripping the Islamic Republic of its nuclear capabilities were completely at odds with each other. From Obama’s perspective, he was offering Khamenei an irresistible deal: a strategic accommodation with the United States. Iran analysts had led the president to believe that Khamenei was desperate for just such an accommodation, and to achieve that prize he was searching only for a “face-saving” nuclear program—one that would give him a symbolic enrichment capability, nothing more. What soon became clear, however, was that Khamenei was betting that Obama would accommodate Iran even if it insisted on, and aggressively pursued, an industrial-scale program.
In theory, Khamenei’s intransigence could have handed Obama an opportunity. He could admit the “train wreck”—namely, that Round Two of his Iran engagement had followed the disastrous pattern set by Round One—and begin working with Congress and our despairing allies to regain lost leverage. This he obviously declined to do. Instead, he has chosen to keep the negotiating process alive by retreating further. Rather than leaving the table, he has paid Iran to keep negotiating—paid literally, in the form of sanctions relief, which provides Iran with $700,000,000 per month in revenue; and figuratively, with further concessions on the nuclear front.
Over the last year, Obama has reportedly allowed Iran to retain, in one form or another, its facilities at Natanz, Fordow, and Arak—sites that Iran built in flagrant violation of the NPT to which it is a signatory. This is the same Obama who declared at the outset of negotiations that the Iranians “don’t need to have an underground, fortified facility like Fordow in order to have a peaceful nuclear program. They certainly don’t need a heavy-water reactor at Arak in order to have a peaceful nuclear program. . . . And so the question ultimately is going to be, are they prepared to roll back some of the advancements that they’ve made.” The answer to his question, by now, is clear: the Iranians will not roll back anything.
The president believes that globalization and economic integration will induce Tehran to forgo its nuclear ambitions. Meanwhile Iran’s rulers are growing stronger, bolder, and ever closer to nuclear breakout capacity.
For a majority in Congress, and for all of America’s allies in the Middle East, this fact is obvious, and it leads to an equally obvious conclusion: the only way to salvage the West’s position in the nuclear negotiations is to regain the leverage that the president’s deferential approach has ceded to Iran. With this thought in mind, a large group of Senators is currently supporting legislation that will make the re-imposition of sanctions mandatory and immediate if the Iranians fail to make a deal by the time the current term of the JPOA lapses.
In an effort to bolster that initiative, Speaker of the House John Boehner invited Benjamin Netanyahu to Washington to address Congress on Iran. Netanyahu accepted the invitation without first consulting the White House, which reacted in a storm of indignation, describing the move as an egregious break in protocol and an insult to the president. Instead of trying to paper over the disagreement, Obama has done everything in his power to advertise it. In making his personal rift with Netanyahu the subject of intense public debate, the White House means to direct attention away from the strategic rift between them—and from the fact that the entire Israeli elite, regardless of political orientation, as well as much of the U.S. Congress, regards the president’s conciliatory approach to Iran as profoundly misguided.
Meanwhile, the president is depicting his congressional critics as irresponsible warmongers. He would have us believe that there are only two options: his undeclared détente with Iran and yet another war in the Middle East. This is a false choice. It ignores the one policy that every president since Jimmy Carter has pursued till now: vigorous containment on all fronts, not just in the nuclear arena. Obama, however, is intent on obscuring this option, and for a simple reason: an honest debate about it would force him to come clean with the American people and admit the depth of his commitment to the strategy whose grim results are multiplying by the day.
As a matter of ideology as much as strategy, Obama believes that integrating Iran into the international diplomatic and economic system is a much more effective method of moderating its aggressive behavior than applying more pressure. Contrary to logic, and to all the accumulated evidence before and since the November 2013 interim agreement, he appears also to believe that his method is working. In his March 2014 interview, he argued that his approach was actually strengthening reformers and reformist trends in Tehran: “[I]f as a consequence of a deal on their nuclear program,” he said, “those voices and trends inside of Iran are strengthened, and their economy becomes more integrated into the international community, and there’s more travel and greater openness, even if that takes a decade or 15 years or 20 years, then that’s very much an outcome we should desire.”
Perhaps the president is correct. Perhaps globalization will remove the roughness from the Islamic Republic just as ocean waves polish the jagged edges of shells. If so, however, it will happen on much the same, oceanic schedule. In the meantime, the seasoned thugs in Tehran whom the president has appointed as his strategic partners in a new world order grow stronger and bolder: ever closer to nuclear breakout capacity, ever more confident in their hegemonic objectives. On condition that they forgo their nuclear ambitions, the president has offered them “a path to break through [their] isolation” and become “a very successful regional power.” They, for their part, at minuscule and temporary inconvenience to themselves, have not only reaped the economic and diplomatic rewards pursuant to participation in the JPOA but also fully preserved those nuclear ambitions and the means of achieving them. Having bested the most powerful country on earth in their drive for success on their terms, they have good reason to be confident.
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Life on the Edge
By John Mauldin | May 14, 2016
“Where justice is denied, where poverty is enforced, where ignorance prevails, and where any one class is made to feel that society is an organized conspiracy to oppress, rob and degrade them, neither persons nor property will be safe.”
– Frederick Douglass
“I am for doing good to the poor, but I differ in opinion about the means. I think the best way of doing good to the poor is not making them easy in poverty, but leading or driving them out of it.”
– Benjamin Franklin

Like many of you, I’m trying to understand an economic landscape that’s changing by the day – and rarely for the better, at least from the standpoint of the middle and lower classes. I am also trying to understand how in the world the two great US political parties have conspired to give us a choice, as Peggy Noonan has said, of “Crazy Man vs. Criminal.”
I think these two questions are related, and not just in the United States. Populist angst is taking hold around the world. Like all anger, it isn’t necessarily rational and may not bring the desired changes, but the anger and frustration are real. People have real problems, and increasingly they don’t trust traditional leaders to solve them.
Last week I had the privilege of meeting first privately and then publicly with Peggy Noonan. For those who don’t know, she was President Reagan’s speech writer and is now a Wall Street Journal columnist and celebrated author. As a writer, she is one of my heroes, perhaps the greatest essayist of my generation – a true wordsmith.
Back in February, with the presidential campaign in full force, Peggy wrote a column that has been on my mind ever since. She titled it “Trump and the Rise of the Unprotected.” Everyone should read it, preferably several times. It is that good.
Whatever you think of Donald Trump, he is a symptom of larger trends. So is Bernie Sanders. A major fraction of the population is living on the edge, vulnerable and unprotected. Most of you reading this letter aren’t in that category; you have homes, steady incomes, and some investment capital. That puts you way ahead of average.
Today we’re going to look at the real-world economic pain that so many people experience in daily life. Some of this will be hard reading, but it’s important. Reading it, you will better understand what is going wrong and how badly we need solutions. You may also come away with a better idea of the direction this country is headed if we don’t see real change in the near future.
Many establishment types in both the Republican and Democratic parties seem to think that Donald Trump and Bernie Sanders are anomalies. That goes double for the Republican Party establishment class that thinks their money can control things. Trump is not an anomaly; he is a harbinger of a growing frustration that is bigger than corporate donors and super PACs.
Peggy Noonan says the current unrest is the logical progression of trends that began long ago. The upper stratum of society is increasingly “protected” from sharing, and often even from seeing, the travails of daily life as most people experience them. Here is how she describes our situation (the boldface emphasis is mine):
There are the protected and the unprotected. The protected make public policy. The unprotected live in it. The unprotected are starting to push back, powerfully.
The protected are the accomplished, the secure, the successful – those who have power or access to it. They are protected from much of the roughness of the world. More to the point, they are protected from the world they have created. Again, they make public policy and have for some time.
I want to call them the elite to load the rhetorical dice, but let’s stick with the protected.
They are figures in government, politics and media. They live in nice neighborhoods, safe ones. Their families function, their kids go to good schools, they’ve got some money. All of these things tend to isolate them, or provide buffers. Some of them – in Washington it is important officials in the executive branch or on the Hill; in Brussels, significant figures in the European Union – literally have their own security details.
Because they are protected they feel they can do pretty much anything, impose any reality. They’re insulated from many of the effects of their own decisions.
This insulation is now so common we don’t even notice it – and not just in government. Business executives meet in a nice office, tweak a few numbers, and somewhere down the line people lose their jobs. Those folks are thousands of miles away, and the decision-makers never even see them. This is what it means to be “protected.”
Peggy goes on to explain why immigration is such a watershed issue.
Many Americans suffered from illegal immigration – its impact on labor markets, financial costs, crime, the sense that the rule of law was collapsing. But the protected did fine – more workers at lower wages. No effect of illegal immigration was likely to hurt them personally.
It was good for the protected. But the unprotected watched and saw. They realized the protected were not looking out for them, and they inferred that they were not looking out for the country, either.
The unprotected came to think they owed the establishment – another word for the protected – nothing, no particular loyalty, no old allegiance.
Mr. Trump came from that.
Loyalty and allegiance flow in both directions. Yet somehow we’ve reached a point where the people who make decisions are so separated from the people who pay the cost of those decisions that neither group feels any loyalty to the other at all. This is not a recipe for a stable social order and a thriving economy.
I want to take Ms. Noonan’s thoughts a little further. The protected are not just the politicians and bureaucrats who make and execute public policy; they are all the people who, because of their jobs and income, can generally protect themselves from the vagaries and vicissitudes of life. They have the money to hire the lawyers, doctors, mechanics, pay for the insurance, etc., to deal with whatever problems arise.
Are you in the protected class? If you’re reading this newsletter, you probably are. At least for now. I do have some readers who are struggling. I read their comments online and sometimes get email from them. For the most part, though, people read me because they have money to invest and want to keep up with economic news. The unprotected have other priorities.
I think we have subcategories within the protected class, though. I know some of the top 0.1%, and their lives are not like mine. They have multiple mansions, bodyguards, private jets, chauffeurs, and people to take care of everything. Call them the Super-protected.
As for me, I’m just plain protected. I live in a nice apartment with a doorman downstairs. I have assistance to help me with a lot of the “busywork.” I don’t miss any meals unless I’m trying to lose weight. I drive my own well-used vehicle. I don’t rate a private jet, but I can at least fly first class, usually, as my frequent flyer status with American Airlines allows me to be upgraded a large percentage of the time.
Another step down are what we might call the “semi-protected.” These are people with secure jobs, college degrees, some money in the bank, and a modicum of leisure time. They have the luxury of wondering where Junior will go to college instead of whether they can even pay for it.
Those three categories encompass maybe (being generous) 30% of the population. The rest are the unprotected. What is life like for them? It’s a surprisingly hard question. You can’t truly know unless you’ve lived it, but I found one very interesting account in The Atlantic magazine. The May 2016 cover story is “The Secret Shame of the Middle Class.”

The writer, Neal Gabler, starts by noting a Federal Reserve survey that found 47% of Americans wouldn’t be able to cover an unexpected $400 expense without borrowing or selling something. (That percentage is strikingly, even eerily, similar to the one in the 2012 Mitt Romney quote about the percentage of Americans who are dependent on government but pay no income tax.)
Read that again. Yes, nearly half the country can’t come up with $400 cash in an emergency. That’s stunning. The slightest mishap – a toothache, a minor car problem, a hot-summer electric bill – will send them into debt or force them to sell something.
Gabler says he knows how it feels because he is one of those people:
I know what it is like to have to juggle creditors to make it through a week. I know what it is like to have to swallow my pride and constantly dun people to pay me so that I can pay others. I know what it is like to have liens slapped on me and to have my bank account levied by creditors. I know what it is like to be down to my last $5 – literally – while I wait for a paycheck to arrive, and I know what it is like to subsist for days on a diet of eggs.
I know what it is like to dread going to the mailbox, because there will always be new bills to pay but seldom a check with which to pay them. I know what it is like to have to tell my daughter that I didn’t know if I would be able to pay for her wedding; it all depended on whether something good happened. And I know what it is like to have to borrow money from my adult daughters because my wife and I ran out of heating oil.
That’s life on the edge in USA 2016. The data tells us that millions of people live like this or even worse.
I should point out that many of the protected were once unprotected. I certainly spent the first 35 years of my life in the unprotected class. I know what it’s like to wake up at 2 AM with your stomach in a knot as you try to figure out how you’re going to make your little two-person payroll, pay the electric bill before they turn you off, get enough gas in the car to make it to your first sales call – and wonder how you’re going to get one of your clients to pay you early so you can do all these things.
I lived in older mobile homes – not exactly considered even middle-class – (and in fact had my first two daughters while living in them) and was an enthusiastic supporter of the Reagan revolution because I wanted change. (Just for the record, I should note that I voted Democratic in the two presidential elections before that.)
When you have to borrow money at 18% and your taxes seem god-awful high compared to your income, your views on inflation and government participation change. For many years, as a young businessman, I kept a bank account in North Dakota to write checks on because it took between 7 and 10 days for them to clear. The polite term for that is cash management, but back in the day we called it kiting checks. Today, if I wanted to start a business, I could find a lot of people with a great deal of interest in investing. Back then I couldn’t even get a loan on my own signature.
I understand having an old car that requires a lot of maintenance to get you where you need to go. I grew up knowing how to maintain and repair cars, swing a hammer, and do everything else needed to keep my life moving forward. I actually never thought of that approach to life as unusual; it was just normal. But I really didn’t like where I saw our country and economy going.
So I can understand the frustration of people who don’t feel that they are participating in the prosperity and growth of the country. I at least felt like I had a chance. As we’re going to see as we go along in the letter, more and more people are feeling that circumstances – and the people who create those circumstance – are arrayed against them.
You might respond that even impoverished Americans live better than many others around the world. Maybe so. In some countries the poor and downtrodden simply accept their lot and remain happy. Here, we get angry. Why?
I suspect that much of the anger we see is felt by people who thought they would never suffer financially. They were doing well, but then something happened – a job loss, a medical crisis, drug addiction, bad investments, something pushed them down the ladder. Maybe it was their own mistakes, but they don’t like life on the lower rungs and don’t think they should be there.
Neal Gabler goes on to talk about the overriding shame that follows:
You wouldn’t know any of that to look at me. I like to think I appear reasonably prosperous. Nor would you know it to look at my résumé. I have had a passably good career as a writer – five books, hundreds of articles published, a number of awards and fellowships, and a small (very small) but respectable reputation.
You wouldn’t even know it to look at my tax return. I am nowhere near rich, but I have typically made a solid middle- or even, at times, upper-middle-class income, which is about all a writer can expect, even a writer who also teaches and lectures and writes television scripts, as I do. And you certainly wouldn’t know it to talk to me, because the last thing I would ever do – until now – is admit to financial insecurity or, as I think of it, “financial impotence,” because it has many of the characteristics of sexual impotence, not least of which is the desperate need to mask it and pretend everything is going swimmingly. In truth, it may be more embarrassing than sexual impotence.
“You are more likely to hear from your buddy that he is on Viagra than that he has credit-card problems,” says Brad Klontz, a financial psychologist who teaches at Creighton University in Omaha, Nebraska, and ministers to individuals with financial issues. “Much more likely.” America is a country, as Donald Trump has reminded us, of winners and losers, alphas and weaklings. To struggle financially is a source of shame, a daily humiliation – even a form of social suicide. Silence is the only protection.
I’m no psychologist, but I think psychologists would say that suppressing emotions like shame and anxiety, anger and frustration is terrible for your health. I would bet doing so is part of the reason for the rising middle-age death rate I wrote about last year (see “Crime in the Jobs Report”).
Yet I understand why people keep quiet about lifestyle setbacks. Our culture in the US preaches a survival-of-the-fittest “social Darwinism.” We assume people get what they deserve; and if they don’t succeed, it must be their own fault. So it’s no surprise people hide or downplay their misfortune. Gabler is a brave exception on that point.
In fact, material success (or lack thereof) tells us almost nothing about a person’s character, values, intelligence, or integrity. Sometimes good, hard-working people have bad luck. Lazy idiots can have good luck. I don’t know why.
In either case, bad luck is not what enrages so many people. The unprotected are angry because they believe the game is rigged against them. Moreover, they think the protected class rigged has the game.
As bad as the situation is, official data says it’s improving. Just look at the unemployment rate, down to 5% and job openings everywhere.
Those numbers look quite different from the perspective of the unprotected. The data doesn’t account for underemployment, lowered wages, and job insecurity. If you spend a few hours cutting your neighbor’s grass for 50 bucks and don’t make another penny, you still count as “employed” that month.
Gallup has an enlightening statistic. Their Gallup Good Jobs Index measures the percentage of the adult population that works 30+ hours a week for a regular paycheck. It stood at 45.1% when I checked this week.
Last week’s jobs report told us that 62.8% of the civilian noninstitutional population participates in the labor force, and 5% are unemployed, while Gallup tells us only 45.1% have what it considers a “good job.” These aren’t directly comparable datasets, but a rough estimate suggests that maybe a fifth of the labor force is either unemployed or have less-than-good jobs.
The picture gets even murkier. Last week my good friend (and onetime business partner) Gary Halbert reported a new survey from the Society for Human Resource Management. Their data says American workers actually feel pretty good. Some 88% of employees said they were either “very satisfied” or “somewhat satisfied” with their jobs.
Yet the same survey found that 45% were either “likely” or “very likely” to look for a new job in the next year. So it appears their satisfaction is limited. This survey doesn’t include unemployed workers who also aren’t satisfied with their status.
That 5% unemployment number masks a seriously low participation rate, falling productivity, and a serious surge in low-wage service jobs, coupled with a loss of middle-class jobs. It is skewed by the soaring number of temporary workers, involuntarily self-employed workers, and contractors and freelancers in the gig economy who are technically counted as employed. In other words, 5% unemployment today is not your father’s 5% unemployment. There is a reason it feels substantially different.
So millions, dissatisfied with the eroding American Dream, struggle to make ends meet, despite a historically low unemployment rate. Merely finding a job, while necessary and welcome, didn’t begin to solve their problems.
A May 9 Wall Street Journal story reported some research on this point. People who lose jobs in a recession experience a variety of long-lasting effects. Their new jobs often pay them lower wages, and it takes years for them to reach their previous earnings peak. These people are less likely to own a home; they experience more psychological problems; and their children perform worse in school. The WSJ calls this phenomenon wage scarring.

We know from BLS data that about 40 million Americans lost their jobs in the 2007–2009 recession. Many still feel the financial pain, despite having landed new jobs. Says the WSJ:
Only about one in four displaced workers gets back to pre-layoff earning levels after five years, according to University of California, Los Angeles economist Till von Wachter. A pay gap persists, even decades later, between workers who experienced a period of unemployment and similar workers who avoided a layoff. Estimates vary, but by one analysis, people who lost a job during recessions made 15% to 20% less than their nondisplaced peers after 10 to 20 years.
It gets worse. At some point these people will reach retirement age with little or no savings. They will either keep working – possibly in jobs that would otherwise go to younger workers – or they will live frugally and depress overall consumer spending. That’s not good for anyone.
Think about it. These were probably people who had developed an acceptable lifestyle and were likely saving money and being responsible. Then they lost their jobs, and even now that they’re working again, their pay is still 20% lower than it was. It’s tough to maintain that former lifestyle and still save. And when your house is underwater, selling it and moving down is both difficult and gut-wrenching.
Young workers feel a different kind of pain. Too young to have lost jobs in the recession, they reached adulthood in a labor market that doesn’t want them. That is especially true for those without college degrees.
The April jobs report showed a staggering 16.0% unemployment rate for teenagers ages16–19. This sample includes only those who were actively looking for jobs, so these aren’t full-time students. They have either dropped out, or they want to work while in school. They probably aren’t happy with the situation, and their parents aren’t, either.
While central bankers try to create inflation, for the unprotected inflation never disappeared. Last week in Outside the Box, I quoted Rob Arnott’s study that found inflation for most Americans has been running around 3% annually since 1995. That figure includes the four categories that typical workers are most keenly affected by: rent, food, energy, and medical care. (See “Where’s the Beef?”)
I ran across another shocking data point after sharing Rob’s story. It was in a May 8 Wall Street Journal story called “Rising US Rents Squeeze the Middle Class.” It looks at data that shows middle-income renters have it worse than those above or below them. Buried in the middle of the article was this sentence:
In Boston, median asking rents have increased at an annual rate of 13.2% since 2010, far outstripping the 2.4% average annual increase in income.
If Boston reflects other cities, we can see why people complain about rent and sleep on each other’s couches. This kind of steep climb in the cost of living is very hard on people who have little income to spare.
The following chart comes from Sentier Research (via Doug Short). The blue line is real median household income, which now stands at $57,263. That is, half of US households earn less than that. The picture is actually even worse since, as we saw above, the Consumer Price Index understates inflation for low-end households. Nominal wages may be growing – for those who have jobs – but in real terms the unprotected are falling farther behind every year.

When I look at that chart, I don’t wonder that half the country is furious at the protected class; I wonder what took them so long.
Everything I’ve said about the US applies to most of the developed world. The UK will vote next month on whether to exit the European Union, in part because of the perception that EU policies leave UK workers at a disadvantage. Unemployment rates in Southern Europe are astronomically high, even as refugees pour in from the Middle East. Collapsing commodity and energy prices are hitting Canada and Australia very hard.
Yet in all these places, a portion of society is still doing very well. Why is that? One common thread is central bank policy. The Fed, the ECB, and others decided years ago to push rates down and keep them there. Maybe they honestly thought that would help restore growth. It hasn’t, at least not growth that most people can appreciate.
Let’s be generous and say the central banks made an honest mistake. Bernanke, Yellen, Draghi, and colleagues all wanted to help people. At some point, you would think they might have to say, “It hasn’t worked.” Maybe they already say it among themselves but don’t tell us because they want to preserve what is left of their credibility.
I’m sorry, but at this point there isn’t much credibility left to preserve. The unprotected public has lost faith and is rising up, led by populists and demagogues.
The time for wondering where the anger came from is past. We know where it came from, and it’s too strong to stop now. We will all be living on the edge before this is over. Even the protected don’t have unlimited protection.
Conservative and Republican establishment types are trying to tell themselves that Trump is an anomaly. Things will go back to normal in time. But if there aren’t major changes – and I’m really wondering how those changes can happen, especially in a Clinton presidency – what do you think the mood of the voters will be in 2020, after the near statistical certainty of a recession within the next four years? Unemployment will once again be high and climbing; pensions will be threatened left and right; and there will be even more people living on the edge.
I highlighted a recent study that shows the surprisingly higher death rate among middle-aged whites. That rate is the direct result of increased suicides and abuse of drugs and alcohol – all part of the psychological depression process. And then, while researching today’s letter, I ran across a story in the Washington Post with the intriguing title “Death predicts whether people vote for Donald Trump.” It turns out that there is a direct relationship between the middle-aged mortality rates and the percentage of voters who favor Donald Trump in counties where mortality rates are the highest.
That fact becomes more alarming when you look at the context. Over the past decade, Hispanic people have been dying at a slower rate. Black people have been dying at a slower rate; white people in other countries have been dying at a slower rate.

“There’s something happening here; what it is ain’t exactly clear.”
I think we have crossed a political Rubicon. While money is important in the political process, the unprotected have discovered that their votes are even more important. And that there are more of them than there are of the protected. And that, if you’re in the unprotected class, your vote is not for sale.
Anger and frustration are not limited to middle-class voters. They are roiling the ranks of the educated and people you would normally think of as the protected class. There is a growing recognition that the system no longer functions for many Americans. Donald Trump comes along and says he understands and sympathizes with average Americans; and he’s the one who expresses that frustration in terms that a majority of the unprotected can understand. Other candidates may sympathize, too, but what comes out of their mouths sounds like conventional political yak-yak. Whatever you want to say about Donald Trump, when you hear him speak he doesn’t sound like a normal politician.
I keep telling people to toss out their old investment models because the underlying economic tectonic plates are shifting under our feet, making our old models spit out unreliable predictions. So too, it’s time to seriously think about throwing out our models for political predictions, because we’re in the middle of what is likely to be an epic generational shift in voting patterns. Past performance is not indicative of future results. Now we have to apply that maxim to our political forecasts as well.
There is a fascinating quote attributed to Lord Salisbury, who was the Tory prime minister of England during Queen Victoria’s reign. Supposedly, when she said that things must change, he rejoined, “Change? Change? Aren’t things bad enough already?”
That response is generally read as an upper-class Victorian-era conservative reaction to a situation that might threaten his personal status and class. I read that quote now and wonder about the changes looming in our near future. I wonder whether we’ll look back in 10 years and wish we hadn’t wanted things to change so much. – especially when we’re so uncertain as to what the overall outcome of all that change will be. In addition to finding ourselves in the middle of a massive global monetary policy experiment with no clear understanding of what the consequences are, there is a real potential that we may be entering into a period of similar political experimentation. Fasten your seatbelt.
These are among the topics we are going to have to continue to explore in the coming months and years. I think they have all sorts of serious implications for our investments and financial planning.
I will fly to Abu Dhabi tomorrow evening for a series of meetings and speaking engagements. I was surprised to learn that I can fly nonstop from Dallas to Abu Dhabi on Etihad Airways. That’s one of the nice things about being in Dallas – there are very few places in the world I can’t get to either directly or with one stopover. I will let you know about my experience on Etihad.
I then come home and almost immediately go to Raleigh, North Carolina, to speak at the Investment Institute’s Spring 2016 Event. I’m looking forward to hearing John Burbank and Mark Yusko (who will also be at my own conference the same week) and then to being on a panel with them. I also get to meet with my longtime early mentor and friend Bob Mumford, a name from the past that some of you may remember.
After speaking in the afternoon, I make a mad dash for the airport, arrive back in the Dallas late Monday night, and make final preparations for my Strategic Investment Conference, where upwards of 700 of my closest friends will gather to discuss all things macroeconomic and geopolitical. It is going to be a great week! If you won’t be going to the conference, you can have the next best thing: recordings of the speakers, delivered just a few days after SIC 2016 ends. You can order your set here. I should note that the price will go up after the conference. A lot. So just jump on this offer now.
Speaking of the conference, we have had a few people cancel their registrations for last-minute personal reasons, and those cancellations have opened up a number of spots for those who might like to attend. You can call us at 877-631-6311 to register.
It has been an interesting week for me. David Tice reintroduced me to Vikram Mansharamani, the author of the bestseller Boombustology, which is the definitive book on how to spot financial bubbles before they burst. Vikram is now a professor at Yale, but over the years he has held various positions in management consulting, investment banking, and the running of hedge funds. He now focuses on speaking, writing, teaching, and some consulting. He is a fascinating individual, and it is somewhat intimidating to realize that he is only 42. We have a lot of shared friends and not surprisingly share a number of economic concerns. I think I have talked him into coming to my conference this year. I will try to figure out how to plug him in, as you really do want to meet him.
But before Vikram came by for the prime rib and mushrooms dinner we cooked for a few friends, Ed Easterling dropped in, and we compared notes on the world as I was cooking. You have to be careful with Ed. He can move the conversation in an odd direction and then drop a new, startling factoid into the mix, just to get your reaction. I didn’t see this one coming…
The recent North Carolina law that denies transgender people the right to choose which public bathroom they use has been challenged by the US Justice Department. As I understand it, the law actually goes farther than that and removes a lot of other normal protections, but this is the one that makes the headline. After discussing the topic for a minute, Ed asked me a seemingly innocuous question … for which I knew I had been set up. “How many possible genders are there available on Facebook?” I thought a bit and guessed six. Ed smiled and replied, “No, there are 58.”
I called bull, and we immediately jumped onto Google. Sure enough, the first result was from ABC News, with the headline “Here’s a List of 58 Gender Options for Facebook Users.”
What actually happens is that Facebook gives you a choice between male and female and “custom.” In the US, ABC News had so far found 58 options through their diligent research. It gets more interesting, or perhaps confusing. It turns out there 71 gender options in the United Kingdom. I have always suspected that Brits were a little more different than Yanks, and now I have proof. Then again, they may be having a lot more fun than I ever knew about.
My youngest (21) son walked through about that time, and I caught him up on our conversation. He looked at us and said, “I can’t deal with this. I’m having a hard enough time with the choice between Clinton and Trump. I simply can’t deal with gender confusion at the same time.” And then he turned around and walked away. Perhaps you can sympathize.
The evolution of our social mores over the last 1,000 years has been painstaking but, on the whole, considerable. What was acceptable even in the late Middle Ages – along the lines of killing and torturing for revenge, the marriage of 12-year-olds, and droit du seigneur – is now seen as barbaric and highly illegal. My kids and their friends all think it is perfectly silly that homosexuality was once illegal or held to be immoral. Over time, cultures adapt, and I am sure that with a little bit of bending here and there (pun intended), the Republic will survive. I must tell you, I’m far more worried about monetary policy than I am about gender selection.
It’s time to hit the send button. I have a lot of work to do, and I want to actually have some kind of a life tonight as my girlfriend (yes, I have one of those now and have had for quite some time) and I are going to grill some steaks for friends and just chill. You have a great week!
Your more confused than ever analyst,

+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++3)
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
ARLINGTON
CEMETERYJeopardy
Question:On
Jeopardy the other night, the final question was
"How many steps does the guard take during his
walk across the tomb of the Unknowns?"
All
three contestants missed it!This is
really an awesome sight to watch if
you've never had the chance.
Fascinating. Tomb of the Unknown
Soldier
1.How
many steps does the guard take during his walk
across the tomb of the Unknowns and
why?21
steps:
It
alludes to the twenty-one gun salute which is
the highest honor given anymilitary
or foreign dignitary.2.How long does he hesitate after his about
face to begin his return walk and
why?21
seconds for the same reason as answer number
1
3.Why are his gloves wet?His
gloves are moistened to prevent his losing his
grip on the rifle.4.Does he carry his rifle on the same shoulder
all the time and, if
not, why not?He carries the rifle on the shoulder away
from the tomb. After his march across the path,
he executes an about face and moves the rifle to
the outside shoulder.
5.How often are the guards
changed?
Guards
are changed every thirty minutes,twenty-four hours a day, 365 days a
year.6.
What
are the physical traits of the guard
limited
to?For
a person
to apply for guard duty at the tomb, he must be
between 5'10" and 6'2" tall and his waist size
cannot exceed 30".They
must commit 2 years of life to guard the tomb,
live in a barracks under the tomb, and cannot
drink any alcohol on or off duty for the rest of
their lives. They cannot swear in public for therest of their lives and cannot disgrace theuniform or the tomb in any way.After
two years, the guard is given a wreath pin that
is worn on their lapel signifying they served as
guard of the tomb. There are only 400 presently
worn. The guard must obey these rules for the
rest of their lives or give up the wreath pin.The
shoes are specially made with very thick soles
to keep the heat and cold from their feet. There
are metal heel plates that extend to the top of
the shoe in order to make the loud click as they
come to a halt.There
are no wrinkles, folds or lint on the uniform.
Guards dress for duty in front of a full-length
mirror.The
first six months of duty a guard cannot talk to
anyone nor watch TV. All off duty time is spent
studying the 175 notable people laid to rest in
Arlington National Cemetery. A guard must
memorize who they are and where they are
interred. Among the notables are:President
Taft,
Joe Lewis {the boxer}
Medal of Honor
winner Audie L. Murphy, the most decorated
soldier of WWII and of Hollywood
fame.Every guard spends five hours a day
getting his uniforms ready for guard
duty.
ETERNAL REST GRANT THEM O LORD AND
LET PERPETUAL LIGHT SHINE UPON
THEM.In
2003 as Hurricane Isabelle was
approaching
Washington, DC, our US Senate/House took 2 days
off with anticipation of the storm. On the ABCevening news, it was reported that because
of the dangers from the hurricane, the military
members assigned the duty of guarding the Tomb
of the Unknown Soldier were given permission to
suspend the assignment. They respectfully
declined the offer, "No way, Sir!" Soaked to the
skin,
marching in the pelting rain of a
tropical storm, they said that guarding the Tomb
was not just an assignment, it was the highest
honor that can be afforded
to a service
person.The
tomb has been patrolled continuously,
24/7,
since 1930.God
Bless and keep them.
4)
Specifications:
- Donald John Trump, was born June 14, 1946.
- He will be 70 years old on Election Day.
- From the Internet, he is 6'2" or 6'3' and weighs between 195 and 200 lbs.
- He has a full head of blond/brown hair (which is long and elaborately combed) and blue eyes.
- The Internet tells us he wears a size 12 shoe.
- Donald Trump was born the fourth of five children who were born over eleven years.
- The oldest, Mary Ann, was born in 1937 and is currently a Federal Judge.
- His older brother, Fred Jr, died in early adulthood as a result of complications from alcoholism.
- He has another older sister, Elizabeth and a younger brother, Robert.
- Donald Trump has been married three times.
- Trump's first wife, Ivana, was an immigrant from Czechoslovakia and a divorcee who has been married 4 times in her life. She is a lifelong avid skier and worked in design at the Trump Organization.
- Marla Maples, Trump's second wife is an actress and model
- Trump's third wife, Melania is an immigrant from Slovenia (born in Yugoslavia) and has been a super model.
- Two of Trump's children, Donald Jr and Ivanka, have gone to Penn. Son Eric, went to Georgetown.
- Donald Trump tells us that he is Presbyterian.
- Donald Trump does not appear to have had any interest in occults, mysticism or exotic mythologies.
- Donald Trump's oldest daughter, Ivanka, and her three children are Jewish.
- Trump's oldest daughter, Ivanka, is married to Jared Kushner who is, among other things, a newspaper publisher. The Kushner family is very successful in New York City area real estate.
- Donald's grandmother, mother, first wife, and third wife are all immigrants.
- Donald Trump was born and raised in Queens NY
- Though his family was very wealthy, Trump's boyhood home in the Jamaica Estates section of Queens was not a grand mansion. The Trump home was a larger version of the homes Fred Trump was building for his tenants.
- There are no indications that the Trump family lived among the wealthy elites on vacations or country clubs.
- Queens is the largest of New York's five boroughs and the most ethnically diverse.
- Trump attended a local private day school, the Kew Forrest School, in Queens until about 8th grade.
- His secondary schooling was at New York Military Academy which is about 60 miles north of NYC in Cornwall on the Hudson. He was the class of 1964.
- Trump was never a "Preppie".
- Trump never embraced any aspect of the "Hippie" movement of the time.
- Trump was a very good high school athlete - football, soccer, and especially baseball. He had potential to become a professional baseball player.
- Even in high school - Trump liked women and women liked him
- Trump was generally popular in high school.
- Trump's boarding school room mate liked him.
- He attended Fordham University in NYC for two years and transferred to the University of Pennsylvania's Wharton School of Business.
- At that time, the Wharton School offered a rare program for Real Estate Business.
- Though he was of age, Donald Trump did not serve in Vietnam.
- He was not drafted due to bone spurs in his heels (4F) and also student deferments.
- Ultimately, in the draft lottery, he drew a high number.
- By all we know, Donald Trump does not smoke, drink or use recreational drugs. He'll be the first President in more than 25 years who hasn't smoked weed.
- BTW: Trump's children don't smoke or drink
- Trump makes it well known that he enjoys sexual interaction with women.
- I am unaware that Donald Trump is a recreational gambler.
- His doctor publicly announced Donald to be in excellent health.
I think that to really know Donald Trump, you must know his family background.
The Trump family story is a very American story.
Trump family history - concise version.
- Donald Trump's grandparents immigrated to the U.S. from Alsace (Kallstadt, Germany) which throughout history has been alternately French and German. The Trumps are German, originally speaking the same German dialect as the Amish of Lancaster County, PA.
- His maternal grandparents lived in Scotland.
- Freiderich (Drumph) Trump made a small but respectable fortune in the late 19th Century in the mining boom towns of the American Northwest.
- He returned to Germany to marry his childhood neighbor, Elizabeth Christ.
- The newly married Trumps resettled in the Borough of Queens NY
- Freidrich was establishing a Real Estate business in Queens when he died suddenly at age 49 (1918).
- In 1920, at the age of 15, Fred Trump (Freiderich's son and Donald's father), started a business partnership with his widowed mother called Elizabeth Trump & Son.
- This business was built upon the real estate holdings that his father,Frederich, had amassed (worth about $500,000.00 in today's dollars). This is the original "seed money" of the current Trump Organization.
- Elizabeth & Fred remained close business partners her entire life (she died in 1966).
- In 1936 Fred Trump (age 31) married Mary Ann MacLeod (age 24) of Stoneaway Scotland.
- During the depression, Fred Trump built and successfully operated a supermarket (a new concept at the time) which was sold to King Kullen Co. and operates this day.
- Fred Trump made a lot of money building housing for the military during WWII.
- Fred Trump was investigated by the Justice Department for making "excessive profits" from government contracts.
- All (or nearly all) of the building of Elizabeth Trump & Son's non-government building was residential property in Queens.
- Fred Trump died in 1999 (age 94) - beloved and worth between $250 million and $300 million. His wife died a year later.
"The Donald's" career
Donald Trump is the greatest career achiever of the "baby boomer" generation.
Donald Trump has reached the zenith in his careers as book author, TV entertainer, sports entertainer, Real Estate developer, and currently politician.
- Donald Trump has authored more than 18 books. At least one of them, The Art of the Deal was a top seller.
- Donald says that the Holy Bible is his favorite book. The Art of the Deal is his 2nd favorite book. And The Power of Positive Thinking by Norman Vincent Peale is his third favorite book.
- He likes golf. Donald Trump has developed more than 11 golf courses which bear his name.
- Donald Trump has twice been nominated for an Emmy Award
- Donald Trump has a star on the Hollywood Walk of Fame.
- Donald Trump has been inducted to the Professional Wrestling Hall of Fame.
- Donald Trump has appeared in more than a dozen movies such as Home Alone 2, Zoolander, and Little Rascals
- Donald Trump has been a guest actor in more than 6 TV shows such as Fresh Prince of Bel Air, Days of Our Lives, Sex and the City, and others.
- Trump has been the Executive Producer of 7 TV shows.
- Trump has been the guest host of 5 TV shows such as Extra, Larry King Live, and Saturday Night Live and more.
- Donald Trump has been co-producer of the longest running reality TV show.
- Donald Trump performed in several WWE wrestling shows.
- Donald performed in Wrestlemania 23 which set attendance records and revenue records up til that time.
- In his first candidacy for public office, Donald Trump received the most popular votes for the President of the United States out of a field of experienced and successful politicians. And in most cases, he achieved this with less money than any of his opponents.
Keeping in mind that 90% of startup businesses fail, Trump's record of enterprise is nothing short of amazing.
Donald Trump has enjoyed success in at least 11 very different enterprises: Professional football, Ice Skating rinks, Fragrance, Ice, Steaks, Wines, Model management, Airline, blenders, Men's wear, Bicycle races, world class beauty contests, and many others. In some of these, such as model management, his firm has risen to the top of that particular industry.
- There are 31 buildings that bear his name.
- The largest private real estate development in New York is Trump Riverside. Drive down the Henry Hudson Blvd. - you can't miss them.
- There are at least 12 Trump Towers
- There are at least 6 Trump Plazas.
- There are at least 11 Trump Golf Course developments
- And much, much, more in real estate.
- Trump Entertainment, casinos and resorts was recently sold to Carl Ichan.
- Donald Trump's personal managing of the Wollman Ice Skating Rink project in the early 1980's is the quintessential case study for MBA students in Wharton, Harvard, and other business schools. His performance there was phenomenal.
- Donald Trump's privately held businesses have employed more than 200,000 people.
- In the casino business in Atlantic City, Trump had to do business with known mobsters - and he stayed "clean" and alive.
- Aside from his personal investments, Donald Trump has never been a Wall Street "player".
The Political Trump:
About 1967 - 1987 - Democrat (he was a supporter of Ronald Reagan)
1987 - 1999 - Republican
1999 - 2001 - Reform Party (he supported Ross Perot)
2001 - 2009 - Democrat
2009 - 2011 - Republican
2011 - 2012 - Independent
2012 - Present - Republican
Donald Trump was openly supportive of Mitt Romney's candidacy.
Donald Trump does not seem to hold political party organizations in high regard.
For the most part, his political involvement has been for practical reasons.
Donald Trump does not appear to be held to political ideology.
Some of my take aways:
- Trump has an extraordinarily energetic central nervous system much like Teddy Roosevelt but more targeted to industry and enterprise.
- Trump's presidency will be very energetic, transparent, and communicative.
- Trump will be a very hard working President.
- His interaction with his older brother (who everybody loved) tells me that he thinks that everybody is like him - or wants to be - or should be.
- His relationship with his older brother was a hard lesson in tolerance for him.
- Trump is the Babe Ruth of career achievements.
- He is dumb like a fox. When you think he just said something stupid - he didn't. It's just that you were not his target audience.
- Trump knows the people - the folk.
- His son, Donald Jr. is right. Trump is a "Blue Collar Billionaire".
- More than anything, his TV show, The Apprentice, was his passion. He wants all Americans to have confidence (like he does) to venture.
- Donald Trump is attracted to and marries smart, high achieving women.
- The highest levels of a Trump Administration is certain to have many women - and they will be bright and assertive.
- Donald Trump's children are very important to him. And it shows.
PS. We know less about our current “president” with 2 terms in office.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
5) In the Arena
Pete Hegseth makes an impassioned and experiential argument for how Teddy Roosevelt’s articulation of “good citizens,” “equality of opportunity,” and unapologetic U.S. leadership—“good patriots”—can renew our imperiled American experiment and save the free world, in this fascinating, first-hand challenge to elite progressivism, a historical foreign policy, and status-quo politics.
Despite contention surrounding Teddy Roosevelt’s legacy, Hegseth argues that the Rough Rider’s exhortation serves as a timeless wake-up call for our Republic. Hegseth resurrects Roosevelt’s famous “Citizenship in a Republic” address—best known for the “Man in the Arena” quote—as a road map for addressing the massive challenges facing America today. In order to rejuvenate what makes America exceptional, we must unapologetically get back into Roosevelt’s arena—as engaged “good citizens” at home and powerful “good patriots” in the world.
Bolstered by gripping personal experience, Hegseth channels Teddy Roosevelt’s words to make a case for turning America’s highest ideals into action through the gritty virtues of citizenship, the dogged pursuit of equal opportunity, and aggressive commitment to winning the wars we fight—including the Iraq War. An exceptional American experiment was entrusted to “average citizens” in 1776 and has been perpetuated by every generation since…until now. If we won’t fight for America, then what will we fight for? And if not now, then when? Get in the arena!
- See more at: http://books.simonandschuster.com/In-the-Arena/Pete-Hegseth/9781476749341#sthash.YfOkbhys.dpuf
5) In the Arena
Good Citizens, a Great Republic, and How One Speech Can Reinvigorate America
based on 1 ratings | 1 reviews on Goodreads.com
A vigorous call-to-arms to reignite American citizenship at home and restore American power abroad, using the timeless truths of Teddy Roosevelt’s iconic “Man in the Arena” speech, by the Fox News contributor and decorated Iraq and Afghanistan war veteran.
Pete Hegseth makes an impassioned and experiential argument for how Teddy Roosevelt’s articulation of “good citizens,” “equality of opportunity,” and unapologetic U.S. leadership—“good patriots”—can renew our imperiled American experiment and save the free world, in this fascinating, first-hand challenge to elite progressivism, a historical foreign policy, and status-quo politics.
Despite contention surrounding Teddy Roosevelt’s legacy, Hegseth argues that the Rough Rider’s exhortation serves as a timeless wake-up call for our Republic. Hegseth resurrects Roosevelt’s famous “Citizenship in a Republic” address—best known for the “Man in the Arena” quote—as a road map for addressing the massive challenges facing America today. In order to rejuvenate what makes America exceptional, we must unapologetically get back into Roosevelt’s arena—as engaged “good citizens” at home and powerful “good patriots” in the world.
Bolstered by gripping personal experience, Hegseth channels Teddy Roosevelt’s words to make a case for turning America’s highest ideals into action through the gritty virtues of citizenship, the dogged pursuit of equal opportunity, and aggressive commitment to winning the wars we fight—including the Iraq War. An exceptional American experiment was entrusted to “average citizens” in 1776 and has been perpetuated by every generation since…until now. If we won’t fight for America, then what will we fight for? And if not now, then when? Get in the arena!
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
No comments:
Post a Comment