

Weightiness of Government, inefficiency of bureaucracies
===
It is as if you wanted to paint your house without scraping off six coats of decade's old paint.
Congressional laziness leads to bloat which leads to why so much of our growth is crippled and our economy under performs.
Will anything change? Do not hold your breath.
Congress has no incentive to be efficient and certainly bureaucracies love wallowing in delay and practicing officiousness.
Rube Goldberg is laughing and we will continue to suffer, pay more taxes and watch our ship of state take on more water.
Politicians tell you they want to pass laws which require every new one to replace several old ones but it never happens and never will.
To make matters even worse, Obama tells us climate change is a greater threat than ISIS. But the biggest threat we face is from his expanded and oppressive government.
Obama does not trust people to be free. He, along with most social progressives, believes government has the answers. To accomplish his/their nefarious goal he/they craft legislation that runs into thousands of pages which Congress passes without even reading.
Government is an out of control monster. I submit government is our greatest enemy and America is drowning. This is why a frustrated, angry and indolent citizenry has turned to outsiders as if the ones running are capable of solving the problem. (See 1 below.)
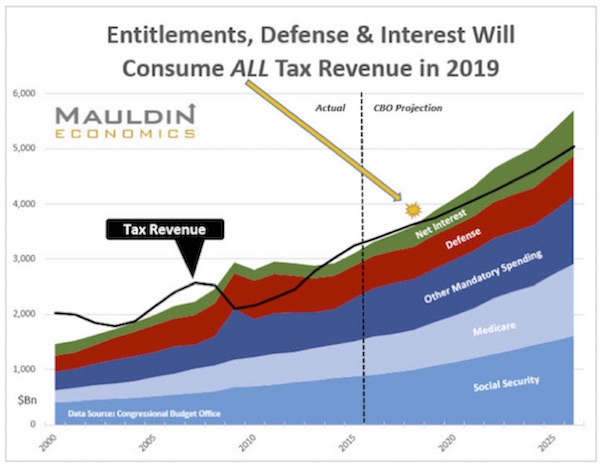
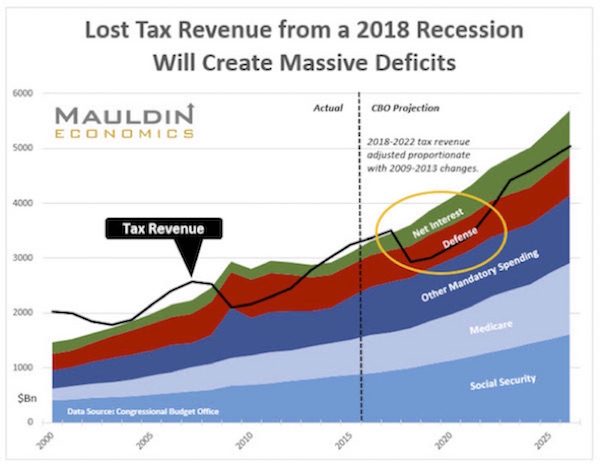
The more optimistic view of our economy. Posted for balance.
My market guru friend seems to have been correct. The near term market did not want to correct and particularly after Yellin was more benign about raising rates. (See 1a below.)
Mauldin's 4th letter to the president. Another view. (See 1b below.)
===
Have a piece of Danish with your gene pool.
Is Dr Sennels a racist?
What would America be like if the Hatfields and McCoys had intermarried with their first cousins as some did? What would America be like if the characters in "Deliverence" were allowed to govern? (See 2 below.)
====
Dick
========================================================================
1)
The Crippling Hold of Old Law
Congress rarely revises or repeals outdated legislation or obsolete programs
Congress is a lazy institution that postures instead of performing its constitutional job to make sure that our laws
actually work, writes Philip K. Howard. PHOTO: ISTOCK
By
Government is broken. So what do we do about it? Angry voters are placing their hopes in outsider
presidential candidates who promise to “make America great again” or lead a “political revolution.”
But new blood in the White House, by itself, is unlikely to fix things. Every president since
under control, to no effect: The federal government just steamed ahead. Red tape got
thicker, the special-interest spigot stayed open, and new laws got piled onto old ones.
What’s broken is American law—a man-made mountain of outdated statutes and
regulations. Bad laws trap daily decisions in legal concrete and are largely responsible for
the U.S. government’s clunky ineptitude.
The villain here is Congress—a lazy institution that postures instead of performing its constitutional
job to make sure that our laws actually work. All laws have unintended negative consequences, but
Congress accepts old programs as if they were immortal. The buildup of federal law since World War
II has been massive—about 15-fold. The failure of Congress to adapt old laws to new realities
predictably causes public programs to fail in significant ways.
The excessive cost of American health care, for example, is baked into legal mandates that encourage
unnecessary care and divert 30% of a health-care dollar to administration. The 1965 law creating
Medicare and Medicaid, which mandates fee-for-service reimbursement, has 140,000 reimbursement
categories today and requires massive staffing to manage payment for each medical intervention,
including giving an aspirin
In education, compliance requirements keep piling up, diverting school resources to filling out forms
and away from teaching students. Almost half the states now have more administrators and support
personnel than teachers. One congressional mandate from 1975, to provide special-education services,
has mutated into a bureaucratic monster that sops up more than 25% of the total K-12 budget, with
little left over for early education or gifted programs.
Why is it so difficult for the U.S. to rebuild its decrepit infrastructure? Because getting permits for a
project of any size requires hacking through a jungle of a dozen or more agencies with conflicting
legal requirements. Environmental review should take a year, not a decade.
Most laws with budgetary impact eventually become obsolete, but Congress hardly ever reconsiders
them. New Deal farm subsidies had outlived their usefulness by 1940 but are still in place, costing
taxpayers about $15 billion a year. For any construction project with federal funding, the 1931 Davis-
Bacon law sets wages, as matter of law, for every category of worker.
Bringing U.S. law up-to-date would transform our society. Shedding unnecessary subsidies and
ineffective regulations would enhance America’s competitiveness.
Eliminating unnecessary paperwork and compliance activity would unleash individual initiative for
making our schools, hospitals and businesses work better. Getting infrastructure projects going would
add more than a million new jobs.
But Congress accepts these old laws as a state of nature. Once Democrats pass a new social program,
they take offense at any suggestion to look back, conflating its virtuous purpose with the way it
actually works. Republicans don’t talk much about fixing old laws either, except for symbolic votes to
repeal Obamacare. Mainly they just try to block new laws and regulations. Statutory overhauls occur
so rarely as to be front-page news.
No one alive is making critical choices about managing the public sector. American democracy is
largely directed by dead people—past members of Congress and former regulators who wrote all the
laws and rules that dictate choices today, whether or not they still make sense.
Why is Congress so incapable of fixing old laws? Blame the founding fathers. To deter legislative
overreach, the Constitution makes it hard to enact new laws, but it doesn’t provide a convenient way
to fix existing laws. The same onerous process for passing a new law is required to amend or repeal
old laws, with one additional hurdle: Existing programs are defended by armies of special interests.
Today it is too much of a political struggle, with too little likelihood of success, for members of
Congress to revisit any major policy choice of the past. That’s why Congresscan’t get rid of New Deal
agricultural subsidies, 75 years after the crisis ended.
This isn’t the first time in history that law has gotten out of hand. Legal complexity tends to breed
greater complexity, with paralytic effects. That is what happened with ancient Roman law, with
European civil codes of the 18th century, with inconsistent contract laws in American states in the first
half of the 20th century, and now with U.S. regulatory law.
The problem has always been solved, even in ancient times, by appointing a small group to propose
simplified codes. Especially with our dysfunctional Congress, special commissions have the enormous
political advantage of proposing complete new codes—with shared pain and common benefits—while
providing legislators the plausible deniability of not themselves getting rid of some special-interest
freebie.
History shows that these recodifications can have a transformative effect on society. That is what
happened under the simplifying reforms of the Justinian code in Byzantium and the Napoleonic code
after the French Revolution. In the U.S., the establishment of the Uniform Commercial Code in the
1950's was an important pillar of the postwar economic boom.
But Congress also needs new structures and new incentives to fix old law. The best prod would be an
amendment to the Constitution imposing a sunset—say, every 10 to 15 years—on all laws and
regulations that have a budgetary impact. To prevent
Congress from simply extending the law by blanket reauthorization, the amendment should also
prohibit reauthorization until there has been a public review and recommendation by an independent
commission of citizens.
Programs that are widely considered politically untouchable, such as Medicare and Social Security, are
often the ones most in need of modernization—to adjust the age of eligibility for Social Security to
account for longer life expectancy, for example, or to migrate public health care away from inefficient
fee-for service reimbursement. The political sensitivity of these programs is why a mandatory sunset is
essential; it would prevent Congress from continuing to kick the can down the road.
The internal rules of Congress must also be overhauled. Streamlined deliberation should be encouraged
by making committee structures more coherent, and rules should be changed to let committees
become mini-legislatures, with fewer procedural roadblocks, so that legislators can focus on keeping
existing programs up-to-date.
Fixing broken government is already a central theme of this presidential campaign. It is what voters
want and what our nation needs. A president who ran on a platform of clearing out obsolete law would
have a mandate hard for Congress to ignore.
— Mr. Howard is the founder of the advocacy group Common Good and the author, most recently, of
“The Rule of Nobody.”
1a)
1a)
| |
| |
|
===========================================================
2)THIS ARTICLE, WRITTEN BY A DANISH PSYCHOLOGIST, PRESENTS A POINT OF VIEW..
Dr. Nicolai Sennels is a Danish psychologist who has done extensive research into a little-known problem in the
Muslim world: the disastrous results of Muslim inbreeding brought about by the marriage of first-cousins.
This practice, which has been prohibited in the Judeo-Christian tradition since the days of Moses, was
sanctioned by Muhammad and has been going on now for 50 generations (1,400 years) in the Muslim world.
This practice of inbreeding will never go away in the Muslim world, since Muhammad is the ultimate example
and authority on all matters, including marriage.
The massive inbreeding in Muslim culture may well have done virtually irreversible damage to the Muslim gene
pool, including extensive damage to its intelligence, sanity, and health.
According to Sennels, close to half of all Muslims in the world are inbred. In Pakistan , the numbers approach
70%.
Even in England , more than half of Pakistani immigrants are married to their first cousins.In Denmark the
number of inbred Pakistani immigrants is around 40%.
The numbers are equally devastating in other important Muslim countries:
67% in Saudi Arabia ;
64% in Jordan ;and Kuwait ;
63% in Sudan ;
60% in Iraq ; and
54% in the United Arab Emirates and Qatar
According to the BBC, this Pakistani, Muslim-inspired inbreeding is thought to explain the probability that a
British Pakistani family is more than 13 X's as likely to have children with recessive genetic disorders.
While Pakistanis are responsible for 3% of the births in the UK , they account for 33% of children with genetic
birth defects.
The risk of what are called autosomal recessive disorders such as cystic fibrosis and spinal muscular atrophy is
18 times higher and the risk of death due to malformations is 10 times higher.
Other negative consequences of inbreeding include a 100% increase in the risk of still births and a 50%
increase in the possibility that a child will die during labour.
Lowered intellectual capacity is another devastating consequence of Muslim marriage patterns.
According to Dr. Sennels, research shows that children of consanguineous marriages lose 10-16 points off their
IQ and that social abilities develop much slower in inbred babies.
The risk of having an IQ lower than 70, the official demarcation for being classified as "retarded",increases by an
astonishing 400% among children of cousin marriages.
(Similar effects were seen in the Pharaonic dynasties in ancient Egypt and in the British royal family, where
inbreeding was the norm for a significant period of time.)
In Denmark , non-Western immigrants are more than 300% more likely to fail the intelligence test required for
entrance into the Danish army
Dr. Sennels says that "the ability to enjoy and produce knowledge and abstract thinking is simply lower in the
Islamic world."
He points out that the Arab world translates just 330 books every year, about 20% of what Greece alone does.
In the last 1,200 years of Islam, just 100,000 books have been translated into Arabic, about what Spain does in
a single year. Seven out of 10 Turks have never even read a book
Dr. Sennels points out the difficulties this creates for Muslims seeking to succeed in the West. "A lower IQ,
together with a religion that denounces critical thinking, surely makes it harder for many Muslims to have
success in our high-tech knowledge societies."
Only nine Muslims have ever won the Nobel Prize, and five of those were for the "Peace Prize." According to
Nature magazine, Muslim countries produce just 10% of the world average when it comes to scientific research
(measured by articles per million inhabitants).
In Denmark ,(Dr. Sennels' native country) Muslim children are grossly over-represented among children with
special needs.
One-third (33%) of the budget for Danish schools is consumed by special education, and anywhere from 51%
to 70% of retarded children with physical handicaps in Copenhagen have an immigrant background.
Learning ability is severely affected as well. Studies indicated that 64% of school children with Arabic parents
are still illiterate after 10 years in the Danish school system. The immigrant drop-out rate in Danish high schools
is twice that of the native-born.
Mental illness is also a product. The closer the blood relative, the higher the risk of schizophrenic illness. The
increased risk of insanity may explain why more than 40% of the patients in Denmark's biggest ward for
clinically insane criminals have an immigrant background.
The U.S. is not immune. According to Sennels, "One study based on 300,000 Americans shows that the
majority of Muslims in the USA have a lower income, are less educated, and have worse jobs than the
population as a whole."
Dr. Sennels concludes:
"There is no doubt that the wide spread tradition of first cousin marriages among Muslims has harmed the gene
pool among Muslims.
Because Muslims' religious beliefs prohibit marrying non-Muslims and thus prevents them from adding fresh
genetic material to their population, the genetic damage done to their gene pool since their prophet allowed first
cousin marriages 1,400 years ago are most likely massive. [This has produced] overwhelming direct and
indirect human and societal consequences."
Bottom line: Islam is not simply a benign and morally equivalent alternative to the Judeo-Christian tradition.
As Dr. Sennels points out, the first and biggest victims of Islam are Muslims.
Simple Christian compassion for Muslims and a common-sense desire to protect Western civilization from the
ravages of Islam dictate a vigorous opposition to the spread of this dark and dangerous religion.
These stark realities must be taken into account when we establish public polices dealing with immigration from
Muslim countries.
====================================================================================





No comments:
Post a Comment